Figure 1. The human HOX transcriptome.
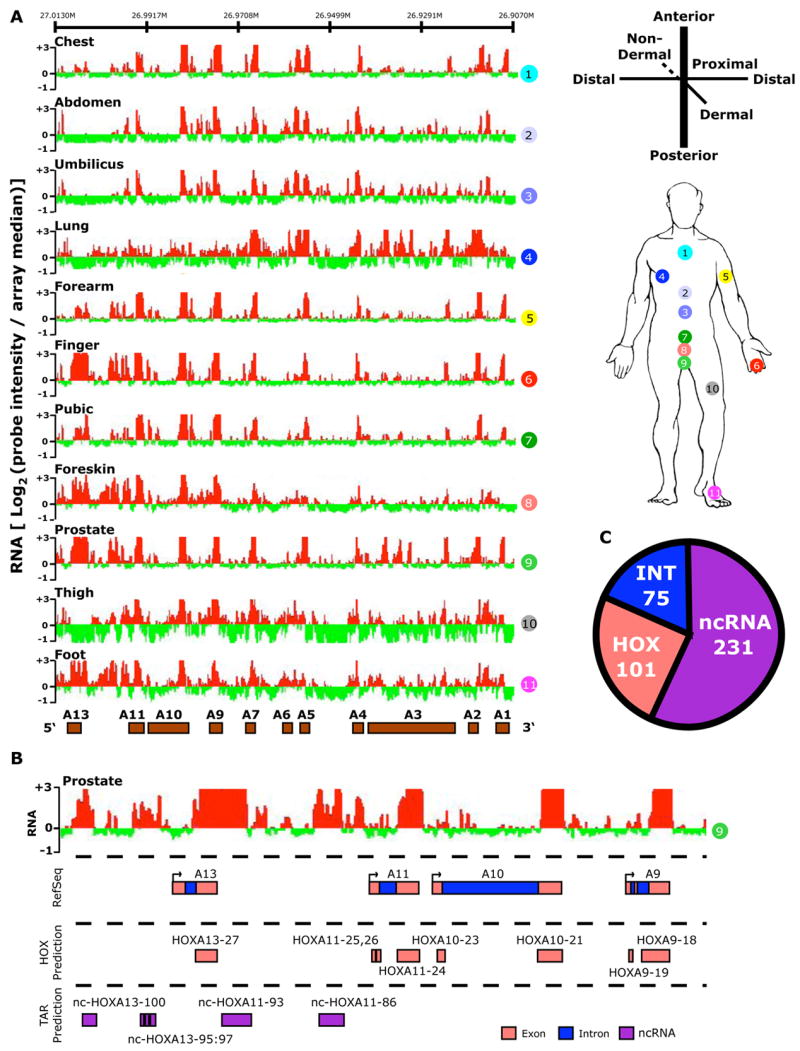
(A) Site-specific transcription of the HOXA locus. Left: The hybridization intensity of 50,532 probes that tile the human HOXA locus for each of the 11 samples (numbered in circles). The intensity of each probe is displayed as the log2 of the ratio of the individual probe intensity divided by the average intensity of all 301,027 probes on the array. The log2 ratio of each probe was averaged over a 100 bp window; red and green bars indicate expression above or below the array mean, respectively. Genomic locations of protein-coding HOX genes are displayed as brown boxes. Right: Anatomic origins of the 11 fibroblast samples with respect to the developmental axes. (B) Transcribed regions were identified by contiguous signals on tiling array, then compared with Refseq sequence to define genic [exonic (pink color) and intronic (blue)] and intergenic transcribed regions (purple). Each predicted HOX exon or intron was named HOXn or int-HOXn, respectively. Intergenic transcribed regions were named as nc-HOXn where n is the HOX paralog located 3′ to the ncRNA on the HOX coding strand. (C) Summary of transcribed regions in all four HOX loci defining the number of HOX genic, intronic, and ncRNA transcribed regions.
