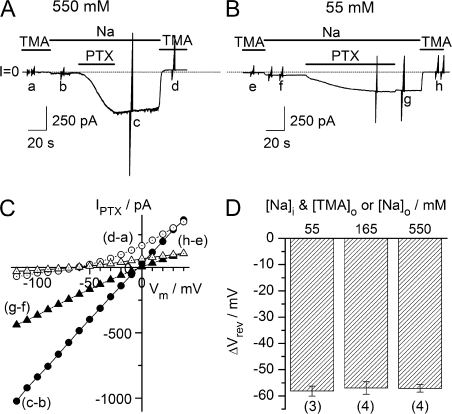
Figure 3.
The Na+/TMA+ biionic potential is independent of the absolute concentration of these permeant ions. (A and B) Outside-out patches from giant fiber lobe neurons held at −50 mV with pipettes containing 550 (A) or 55 (B) mM Na+. Top, horizontal bars designate bath ionic composition and application of palytoxin (10 nM). Bottom, current trace; the dotted line indicates the zero current level, and the brief vertical deflections indicate episodes in which 50-ms-long voltage pulses (−120 to +40 mV in 10-mV increments) were applied. (C) Palytoxin-induced I-V relationships with bath solutions containing 550 mM Na+ (from A; filled circles, c-b), 550 mM TMA+ (from A; open circles, d-a), 55 Na+ (from B; filled triangles, g-f) and 55 TMA+ (from B; open triangles, h-e). (D) Changes in Vrev (VrevTMA+ o − VrevNa+ o) at three different permeant ion concentrations. Mean values (number of experiments given in parentheses) were −58 ± 2, −57 ± 3, and −57 ± 1 mV for permeant ion concentrations of 55, 165, and 550 mM, respectively.