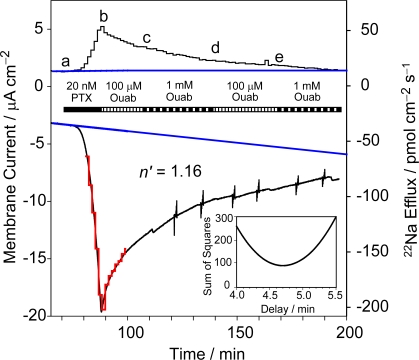
Figure 5.
Determination of the flux ratio exponent n' for Na/K pump-channels opened by palytoxin. The axon was internally dialyzed with 98 mM Na+ and superfused with 400 mM Na+, and held at 0 mV. Simultaneous measurements of unidirectional 22Na+ efflux (top trace) and net current (bottom trace) were used to estimate the flux ratio exponent n' for Na/K pump-channels opened by 20 nM palytoxin. The inset figure illustrates the procedure to account for the delay between current measurements and the fraction collector that collected radioactive samples. Least-squares fits of Eq. 1 to the current and flux data were repeated for successive 5-s increments of delay, to find the delay time that minimized the sum of squared deviations for the estimate of n'. In this experiment, a time delay of 4.70 min resulted in a minimum in the sum of squares and gave an estimate for n' of 1.16. Baseline values (blue lines) for 22Na+ efflux and net current were used to correct measured values in the determinations of n'. The red trace represents the measured efflux data transformed by Eqs. 1 and 2 using the best-fit n' and delay value obtained from the fits. In the presence of external Na+, saturating concentrations of ouabain fully reverse palytoxin-induced 22Na+ efflux in ∼100 min. Vertical current displacements are in response to voltage staircases, with 0.5 mV steps, from −5 to 5 mV applied to monitor membrane conductance during the decline in current and flux.