Figure 5.
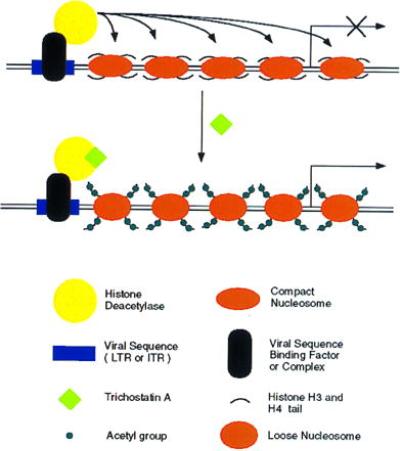
Model for silencing and reactivation of recombinant viral genes. A host protein or protein complex binds to viral sequences (AAV ITRs or retroviral LTRs) and recruits a histone deacetylase to the site through protein–protein interactions. The enzyme deacetylates histone H3 and H4 N-terminal tails, and the resulting change in chromatin structure inhibits expression from adjacent promoters. Treatment with trichostatin A specifically inhibits histone deacetylases. Subsequent acetylation of histones produces a chromatin structure that allows transcription factors to bind to nearby promoters and activate gene expression.
