Figure 5.
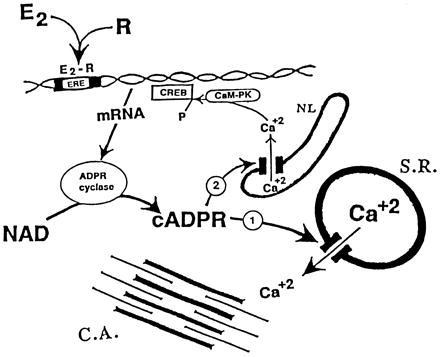
The scheme of the proposed second messenger/modulator role of cADPR in action of E2 upon uterine smooth muscle cell. E2-receptor complex (E2-R) binds to estrogen-responsive element and enhances de novo synthesis of ADPR cyclase. Increased activity of ADPR cyclase catalyzes generation of cADPR from β-NAD and the increased level of cADPR, which then (i) facilitates [Ca2+]i release from sarcoplasmic reticulum (S.R.) and enhances Ca2+-dependent responses of a contractile apparatus (C.A.); (ii) cADPR triggers Ca2+ release from nucleolemmal (NL) space into nucleoplasm, Ca2+ activates calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV (CaM-PK), which phosphorylates the cAMP responsive element binding protein (CREB) (and other transcription factors). Phosphorylated CREB enhances expression of genes that are regulated by estrogen. cADPR may play similar signaling roles in the action of other hormones of steroid superfamily.
