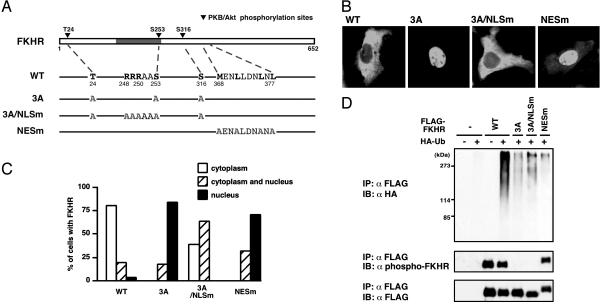
Fig. 4.
Both phosphorylation and cytoplasmic retention are necessary for efficient FKHR ubiquitination. (A) A schematic representation of FKHR point mutants. The gray box indicates the forkhead DNA binding domain. (B) Localization of FKHR WT or mutants was monitored by transfection of these FKHRs into HepG2 cells in the presence of FBS and by immunolocalization with anti-FLAG antibody. (C) For quantitation, 100 cells per coverslips were counted, and the results are shown as the percentage of cells. (D) HepG2 cells were transfected with the indicated FKHR mutant and HA-ubiquitin expression plasmids and treated with MG132 in the presence of FBS. Whole cell extracts were subjected to anti-FLAG immunoprecipitation and followed by anti-HA (Top), anti-phospho-FKHR (Middle), or anti-FLAG (Bottom) immunoblotting.