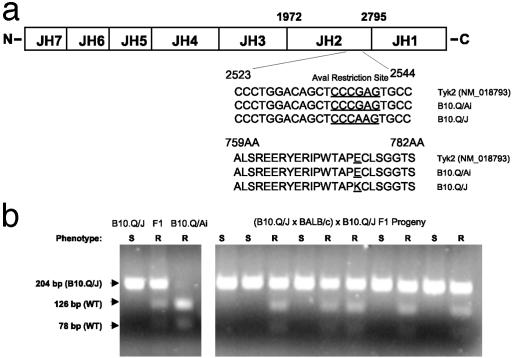
Fig. 2.
B10.Q/J Tyk2 contains a single G→ A mutation in the JH2 domain. (a) Comparison of B10.Q/Ai and B10.Q/J Tyk2 cDNA sequences. Splenic cDNA from B10.Q/Ai and B10.Q/J mice were amplified by PCR by using primers (as described in Materials and Methods) spanning the entire coding region of Tyk2. B10.Q/J mice exhibit a G→ A base substitution at position 2538. An E775K amino acid substitution is predicted in the JH2 domain. Note: The G→ A polymorphism resulted in the loss of an AvaI restriction site present in the wild-type Tyk2 sequence. (b) A 204-bp Tyk2 fragment was amplified from genomic DNA of parental, F1, and F1 backcross progeny (as described in Materials and Methods) and subjected to AvaI restriction typing. The presence of the wild-type Tyk2 allele is indicated by the appearance of 126- and 78-bp AvaI digested fragments. The AvaI-resistant 204-bp PCR product corresponds to the mutant B10.Q/J Tyk2 allele. AvaI digestion patterns for individual parental and F1 mice (Left) and representative backcross mice (Right) are shown. The resistance or susceptibility phenotype of individual mice to T. gondii infection is indicated by R or S, respectively.