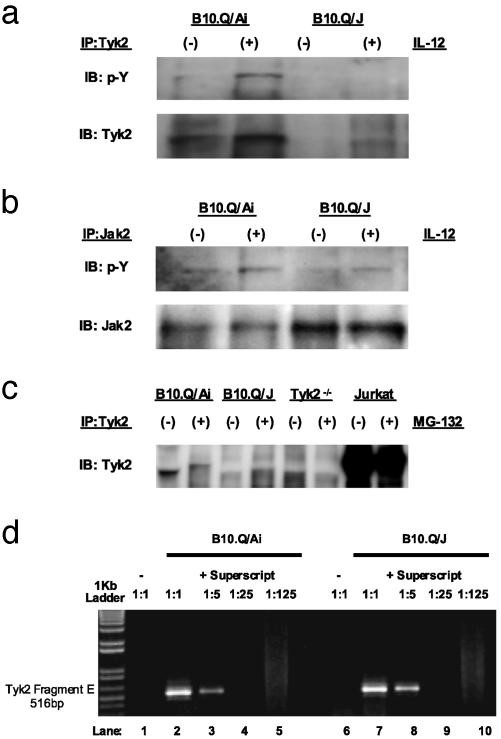
Fig. 4.
Lack of immunoreactive Tyk2 expression in B10.Q/J cells despite the presence of Tyk2-specific transcript. (a and b) T cell blasts from B10.Q/Ai and B10.Q/J mice were cultured with (+) or without (–) IL-12 (50 ng/ml) and analyzed for Tyk2 activation (a) or Jak2 activation (b) by immunoprecipitation with Tyk2- or Jak2-specific Abs and subsequent immunoblotting of precipitates with phosphotyrosine-specific (p-Y) Ab. The same blots were reprobed with Tyk2- and Jak2-specific Abs to control for protein loading. (c) T cell blasts from B10.Q/Ai, B10.Q/J, and Tyk2–/– mice were cultured for 8 h in the presence (+) or absence (–) of proteasome inhibitor MG-132 (10 ng/ml). Total protein extracts were then immunoprecipitated with Tyk2-specific Ab followed by immunoblotting with the same Tyk2 Ab. Jurkat T cells were included to serve as positive control for immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting. (d) B10.Q/J cells have equivalent amounts of Tyk2-specific transcripts compared with wild-type cells. cDNA was prepared from the spleens of B10.Q/Ai or B10.Q/J mice followed by PCR with primers specific for the 3′ terminus of Tyk2 (Fragment E: 2143–2580). cDNA primed with random hexamers in the presence of reverse transcriptase (RT) from both strain of mice was diluted serially (1:5) (lanes 2–5 and 7–10). cDNA primed in the absence of RT lack Tyk2-specific transcripts (lanes 1 and 6).