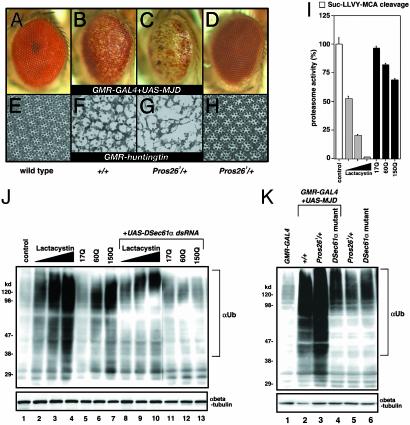
Fig. 2.
The DSec61α translocon is required for the accumulation of undegraded proteins caused by expanded polyglutamine. (A–H) In the fly models for the polyglutamine diseases MJD and Huntington's disease, the partial loss of the 26S proteasome subunit clearly enhanced the phenotypes of neurodegeneration in the eye. Light microscopic (A–D) and semithin section (E–H) images of the compound eyes are shown (day 15 after eclosion). (Magnifications: ×63.) The following genotypes are shown: w;GMR-GAL4/+ (A and E), w;GMR-GAL4/+;UAS-MJD(M)/+ (B), w;GMR-GAL4/+;UAS-MJD(M)/Pros261 (C), w;+/+;Pros261/+ (D and H), w;+/+; GMR-huntingtin120Q/+ (F), and w;+/+;GMR-huntingtin120Q/Pros261 (G). (I) Proteasome activity in Drosophila cells. Plasmids (800 ng) encoding the expanded polyglutamine tracts (httQ17, httQ60, and httQ150) were overexpressed in Drosophila S2 cells with 200 ng of driver plasmid pWAGAL4. Other S2 cells were treated with lactacystin (1, 5, and 20 μM). The proteasome activities (a cleavage activity of Suc-LLVY-MCA; chymotrypsin-like) were measured 24 h after transfection. Enzymatic activity is expressed as the percentage of the activity in control lysates. (J) Immunoblotting of the cell lysates prepared in I with the anti-ubiquitin (αUb) antibody. In some cases, 30 ng of UAS-DSec61α dsRNA and 200 ng of driver plasmid pWAGAL4 were cotransfected. Similar amounts of protein were loaded, as determined by using an anti-β-tubulin (αbeta-tubulin) antibody. (K) The accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins induced by the expanded polyglutamine tracts in the Drosophila eye was remarkably reduced in flies that were transheterozygous for the mutant DSec61α allele. Eighteen fly eyes from each line of the indicated genotype (day 1 after eclosion) were carefully dissected and subjected to immunoblotting with an anti-ubiquitin (αUb) antibody. Similar amounts of protein were loaded, as determined with an anti-β-tubulin (αbeta-tubulin) antibody. The following genotypes are shown: w;GMR-GAL4/+ (lane 1), w;GMR-GAL4/+;UAS-MJD(M)/+ (lane 2), w;GMR-GAL4/+;UAS-MJD(M)/Pros261 (lane 3), w;GMR-GAL4 DSec61αP560/DSec61αEP(2)2567;UAS-MJD(M)/+ (lane 4), w;+/+;Pros261/+ (lane 5), and w;DSec61αP560/DSec61αEP(2)2567;+/+ (lane 6).