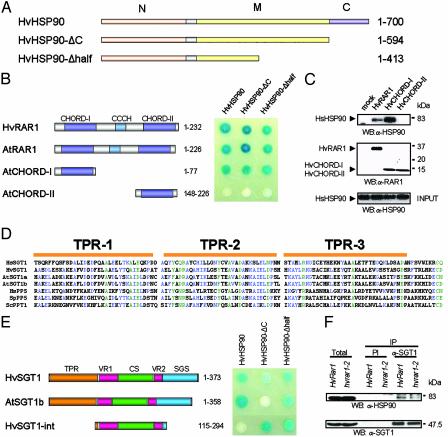
Fig. 1.
Interaction of HSP90 with RAR1 and SGT1. (A) Domain structures of HvHSP90 constructs. Numbers refer to amino acids encoded. N, N-terminal ATPase domain; M, middle substrate binding domain; C, C-terminal for dimerization and cochaperone binding. (B) In vivo interaction analysis of RAR1 and HSP90 by the yeast two-hybrid system. (Left) Domain structures of plant RAR1 constructs. Interactions were performed by using the LexA system with the lacZ reporter gene, expressing RAR1 proteins as binding domain fusions and HvHSP90 proteins as activator domain fusions. (C) In vitro binding assay using HsHsp90 and S-tag RAR1 fusion derivatives. The precipitated proteins were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Molecular mass markers are indicated (in kDa). (D) Sequence alignment of the TPR domain from SGT1 and PP5 proteins: human SGT1 (Hs, residues 10–123, GenBank accession no. AAD30062), barley SGT1 (Hv, 5–118, AAL33610), Arabidopsis SGT1a and SGT1b (At, 1–114, At4g23570 and At4g11260, respectively), human PP5 (Hs, 27–140, AAD22669), Schizosaccharomyces pombe PP5 (Sp, 4–117, T40391), Saccharomyces cerevisiae PPT1 (Sc, 11–124, S52571). Green indicates 100% conserved residues, and blue indicates >50% conserved residues. (E) In vivo interaction analysis of SGT1 and HSP90 by the yeast two hybrid system. Domain structures of HvSGT1 and AtSGT1b made in pLexA vector are shown on the left. Interactions were detected as shown in B. (F) Coimmunoprecipitation of HvSGT1 and HvHSP90 in barley. Protein extract from HvRAR1 or mutant hvrar1–2 barley plants were immunoprecipiated with SGT1 or preimmune (PI) antibodies. Samples of eluted fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies to SGT1 and HSP90.