Figure 4.
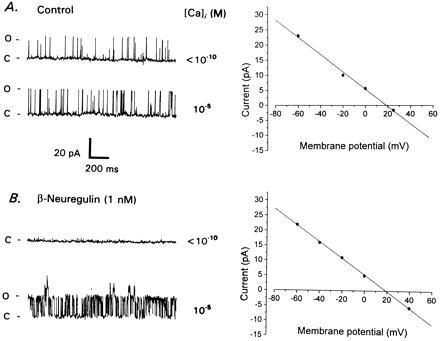
Effects of β-neuregulin on large-conductance K+ channels in developing CG neurons. (A) Inside–out patch recording from E9 neuron cultured for 12 hr in the absence of trophic factor. Traces to the left show large-conductance K+ channels in Ca2+-free saline (Upper Left) and in saline with free Ca2+ buffered to approximately 10 μM (Lower Left). Membrane potential is −60 mV. Note that gating of large-conductance channels is essentially independent of free Ca2+ concentration. These large-conductance channels reverse close to the calculated EK (+17 mV) and have a unitary slope conductance of 285 pS (Right). (B) Inside–out patch from E9 CG neuron cultured for 12 hr with 1 nM β-neuregulin peptide. Patch is quiescent in Ca2+-free saline (Upper Left), but large-conductance channels exhibit high level of activity in the presence of saline containing 10 μM free Ca2+ (Lower Left). Membrane potential is −60 mV. These large-conductance channels reverse close to calculated EK and have a unitary slope conductance of 285 pS (Right).
