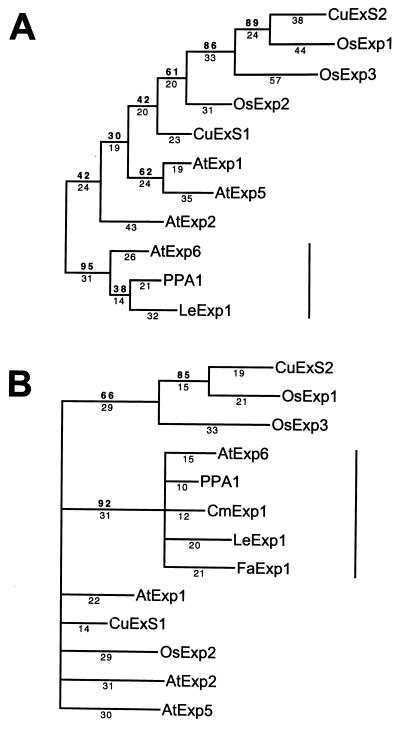
Figure 2.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of full-length deduced amino acid sequences of 11 expansins and homologs. CuExS1 and CuExS2 (Cucumis sativus); OsExp2 and OsExp3 (Oryza sativa); AtExp1, AtExp2, AtExp5, and AtExp6 (Arabidopsis thaliana) all identified in Shcherban et al. (19); PPA1 (Pisum sativum) (28); OsExp1 (Oryza sativa) EMBL accession no. Y07782Y07782. (B) Similar alignment using truncated sequences of the above genes with deduced amino acid sequences of the PCR clones CmExp1 (Cucumis melo) and FaExp1 (Fragaria ananassa) derived from melon and strawberry fruit, respectively. For each alignment, bootstrap analysis used random stepwise addition of taxa with 100 replicates and global (tree bisection and reconnection) branch swapping. Bootstrap confidence values and branch lengths are depicted above and below the lines, respectively. A vertical line represents the position of the expansin subfamily containing three ripening-related genes (LeExp1, CmExp1, and FaExp1).