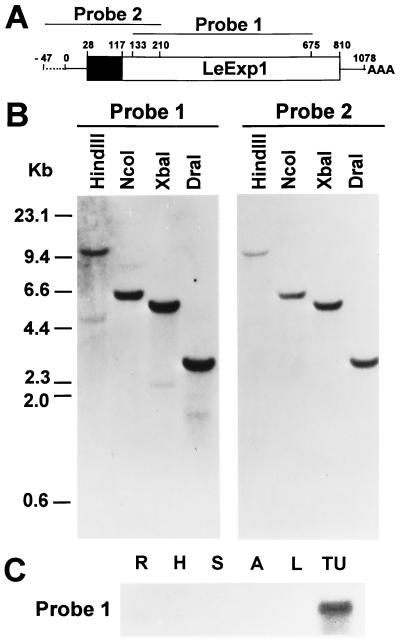
Figure 3.
(A) Diagram of the LeExp1 gene and 47 bp of 5′ flanking sequence derived from the pARC7 and pBluescript II cloning vectors. The boxed region represents the coding sequence with the solid area representing the putative signal sequence. Both 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions are depicted by solid lines and residual cloning vector sequence is depicted by a broken line. Nucleotide numbers are indicated above the gene. Two probes were designed from this sequence and used for Northern and Southern blot analyses. Probe 1 corresponded to a more conserved sequence among expansins while probe 2 corresponded to more divergent sequence. (B) Genomic DNA analysis of LeExp1. Genomic DNA (20 μg per lane) was digested with the indicated restriction enzymes and hybridized with probe 1 and washed at low stringency or with probe 2 and washed at high stringency. (C) RNA gel blot analysis of LeExp1 mRNA abundance in fruit and vegetative tissues. Total RNA (15 μg) from roots (R), hypocotyls (H), stems (S), anthers (A), young leaves (L), or turning fruit (TU) was hybridized, after gel electrophoresis, with probe 1.