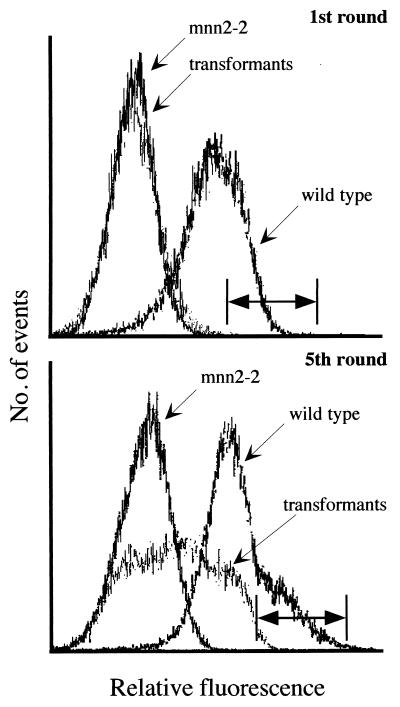
Figure 1.
K. lactis cell surface labeling and separation by FACS. (Upper) Golgi UDP-GlcNAc transporter-deficient K. lactis mutants (KL3; mnn2–2) were transformed with a MDCK cell cDNA library and screened by FACS. Terminal N-acetylglucosamine of wild-type K. lactis (MW103–1C) glycoproteins bind GSII lectin. These cells display higher fluorescence intensity than the UDP-GlcNAc Golgi transporter-deficient mutant. Transformed cells, after one cycle of cell sorting, show a fluorescence profile resembling the transporter-deficient mutant. The horizontal bar indicates the 0.1 percentile of high fluorescence of the transformed cells; cells whose fluorescence spectrum falls in this region were selected for subsequent rounds of cell sorting. (Lower) After five cycles of sorting and selection of the high fluorescence cells, a significant shift in the fluorescence profile of the transformants can be seen into the region of the wild-type cells. Cells whose fluorescence fell in this region, indicated by the horizontal bar, were selected for further analysis of individual clones.