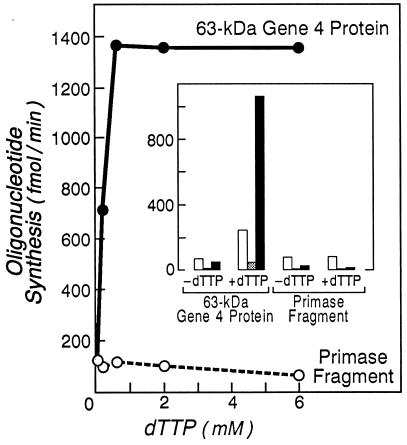
Figure 4.
Effect of dTTP on oligoribonucleotide synthesis. The products of oligonucleotide synthesis assays containing ATP, [α-32P]CTP, and 10 μM 20-base oligonucleotide (5′-GGGTCX15-3′) were separated on 25% polyacrylamide gel containing 2 M urea, and their amounts were measured by using a Fuji BAS1000 Bio-imaging Analyzer. The amounts of di-, tri-, and tetranucleotide synthesized were normalized assuming on labeled nucleotide per dinucleotide (pppAC), two labeled nucleotides per trinucleotide (pppACC), and three labeled nucleotides per tetranucleotide (pppACCC). The rates of oligonucleotide synthesis are shown for reactions catalyzed by the 63-kDa gene 4 protein (•) or the primase fragment (○). (Inset) The rates of dinucleotide (white), trinucleotide (gray), and tetranucleotide (black) synthesis by the 63-kDa gene 4 protein or the primase fragment in the presence and absence of 0.6 mM dTTP.