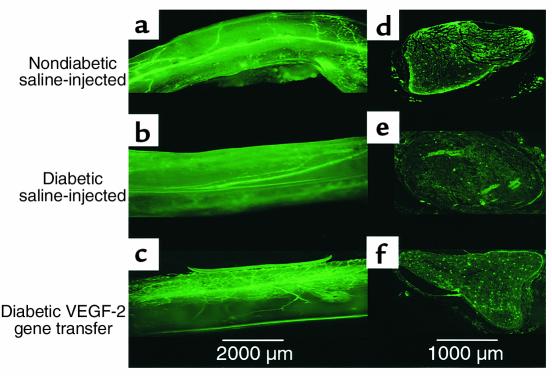
Figure 6.
Representative fluorescence photomicrographs of longitudinal views of whole-mounted rabbit nerves (tibial portion of the sciatic nerve) (a–c) and their respective paraffin-embedded cross sections (d–f) 8 weeks after treatment. Before sacrifice and harvesting of the nerves, in vivo perfusion with FITC-conjugated BS-1 lectin, an endothelial-specific ligand, was performed. (a and d) Samples from a nondiabetic saline-injected control animal, showing a regular pattern of vascularity. (b and e) Samples taken from a diabetic animal 6 months after induction of diabetes and 8 weeks after sham treatment (saline injection). The total network of vasa nervorum is markedly reduced, resulting in an irregular distribution pattern. Note the reduction of stained endoneurial vessels in the cross section. (c and f) Samples from a rabbit after 6 months of diabetes and 8 weeks after VEGF-2 gene transfer. The vascularity appears well preserved, and the number of vessels visible in the cross section appears similar to that of a normal sciatic nerve. ×2 (a–c); ×4 (d–f).