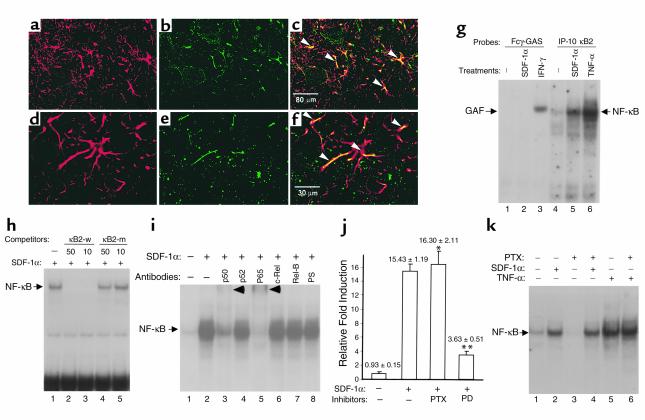
Figure 1.
SDF-1α activates NF-κB in primary astrocytes. (a–f) Immunofluorescence staining of ventral lumbar spinal cord section: anti-GFAP (a and d, red), anti–SDF-1α (b, green), and anti-CXCR4 (e, green). Colocalization of GFAP and SDF-1α (c) or CXCR4 (f) within astrocytes (arrowheads). (g–i) SDF-1α induces NF-κB DNA binding activity. Primary astrocytes were incubated with medium alone or SDF-1α (2 hours) or IFN-γ (250 U/ml; 15 minutes) or TNF-α (30 minutes). Shown are results of EMSA with Fcγ-GAS (g) and IP-10 κB2 probes (g–h). SDF-1α selectively induces NF-κB DNAbinding complex (g) competed by wild-type but not mutant κB elements (h) or supershifted by anti-p50 and anti-p65 antibodies (i). (j) SDF-1α stimulates NF-κB reporter in luciferase activity assay. Primary astrocytes were cotransfected with p6κB-luc and pRL-TK constructs and treated with SDF-1α for 6 hours in the presence or absence of pertussis toxin (PTX) or PD98059 (PD). Shown are mean ± SD(Student’s t test:*PTX + SDF-1α vs. SDF-1α, P = 0.5689; **PD + SDF-1α vs. SDF-1α , P < 0.001). (k) PTX does not suppress SDF-1α- or TNF-α–stimulated activation. Primary astrocytes were treated with SDF-1α for 2 hours or TNF-α for 30 minutes in the presence or absence of PTX. Shown are results of EMSA with IP-10 κB2 probes. Data represent three or more than three experiments (g–k).