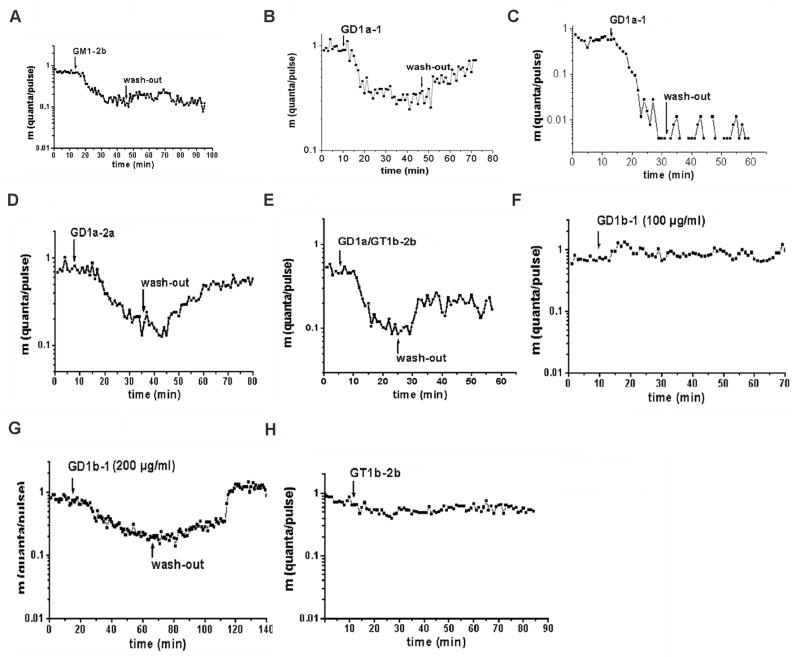
Figure 3.
Effect of anti-GM1 and -GD1a mAbs on presynaptic transmitter release. The time course of evoked quantal release after application of the mAb is shown along with the quanta per pulse, m (logarithmic ordinate scale) versus time in minutes (abscissa). Each point of the curve was determined from the results of at least 256 stimuli; the quantal content (m) was calculated using the Poisson formula. Arrows represent the instant of solution change in the electrode. Evoked quantal release was depressed by GM1-2b (A). mAb GD1a-1 induced a partly reversible block at low concentration (B) and an irreversible blockade at high concentration (C). Different degrees of partly reversible blockade of presynaptic transmitter release occur after application of mAbs GD1a-2a (D) and GD1a/GT1b-2b (E). GD1b-1 at 50–100 μg/ml did not induce any blocking effect (F), but 200 μg/ml induced a completely reversible blockade of evoked quantal release (G). In comparison, presynaptic quantal release was not affected by mAbGT1b-2b (H).