Figure 4. Endothelial Invaginations Result from Podosome-like Protrusive Structures.
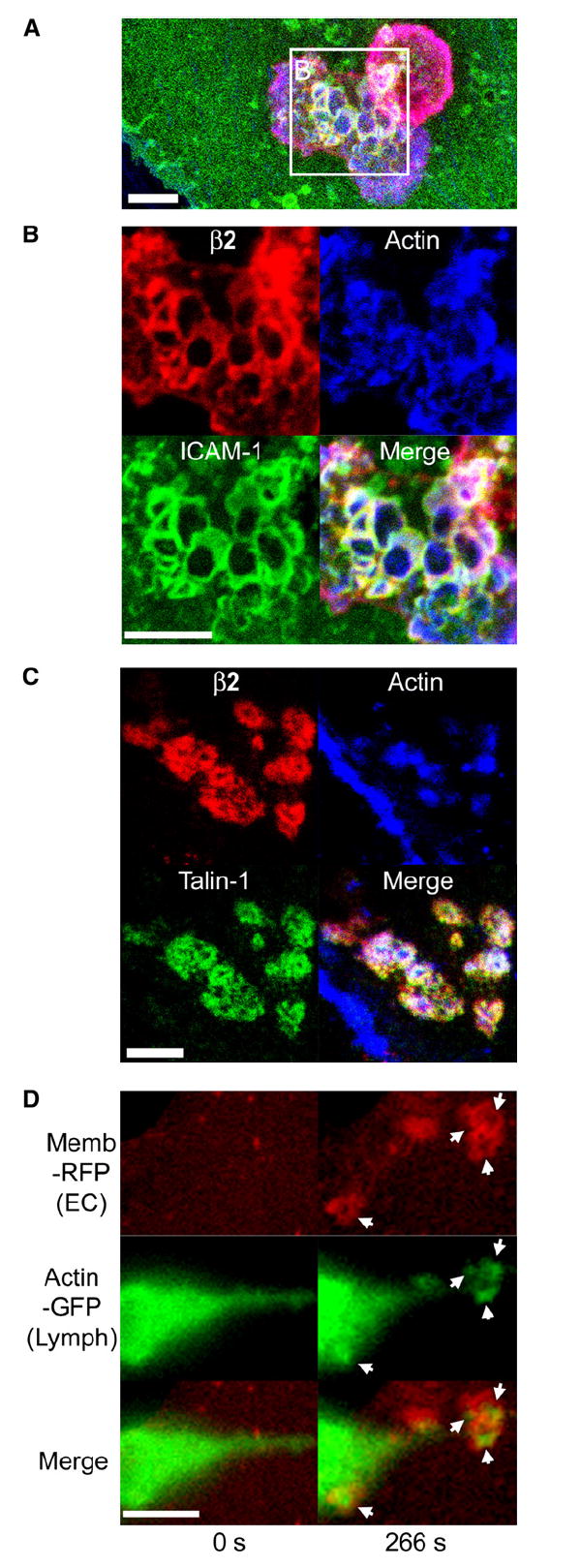
(A–C) Confocal imaging of lymphocyte-endothelial interactions. Lymphocytes were incubated with TNF-α-activated HDMVEC for 5 min followed by fixation, staining for F-actin (blue), leukocyte β2 integrin (red), endothelial ICAM-1 (green in [A] and [B]), or talin-1 (green in [C]), and confocal microscopy described in Experimental Procedures. Images are representative Z-stack projections of confocal sections near the plane of the leukocyte-endothelial interaction interface.
(A) A merged image of β2 integrin, F-actin, and ICAM-1 is shown in which two adjacent lymphocytes, one spread and somewhat dumbbell-shaped (lower left) and one rounded (upper right), adhere to the surface of the endothelium.
(B) An expanded view of the boxed region in (A) is shown as both separate and merged fluorescent channels.
(C) In a separate experiment, samples were stained for β2 integrin, F-actin, and talin-1.
(D) Live-cell imaging of lymphocyte actin. Lymphocytes transiently expressing GFP-actin were incubated with activated HDMVEC expressing memb-RFP and subjected to live-cell imaging. Left and right panels depict a lymphocyte at time points before (relative time point = 0 s) and after (relative time point = 266 s), respectively, endothelial podoprint formation. Memb-RFP, GFP-actin, and merged images are as indicated. Arrows indicate the appearance of podosome-like (Evans et al., 2003) actin puncta in lymphocytes that are centered within the memb-RFP rings of the endothelial podoprints. Note the distinctly green areas (actin) evident at the center of each ring. See corresponding Movie S8. Scale bars represent 5 μm.
