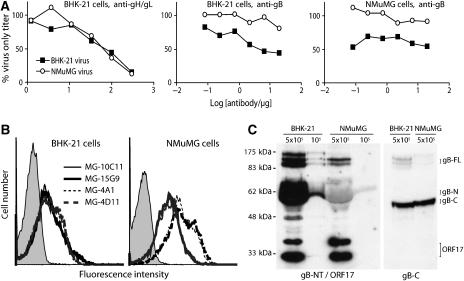
Figure 5.
MuHV-4 virions derived from BHK-21 fibroblasts and NMuMG epithelial cells differ in gB-NT antigenicity and in susceptibility to gB-NT-directed neutralization. (A) Virions from BHK-21 or NMuMG cells were incubated with gH/gL-specific or gB-NT-specific neutralizing mAbs, then titered on BHK-21 or NMuMG cells. The difference in gB-NT-directed neutralization between BHK-21-derived and NMuMG-derived virions was significant by χ2 test for both BHK-21 and NMuMG cells (P<0.002). Equivalent data were also obtained in two further experiments. (B) BHK-21 or NMuMG cells were infected with MuHV-4 and 18 h later analyzed for cell surface gB expression by flow cytometry. MAbs MG-10C11 and MG-15G9 are gB-NT-specific and neutralizing, MG-4A1 and MG-4D11 are not gB-NT-specific and non-neutralizing. The difference in MFI between MG-10C11/MG-15G9 and MG-4A1/MG-4D11 was significantly greater for NMuMG cells (>4-fold) than for BHK-21 cells (<2-fold). Equivalent data were obtained in two further experiments. (C) BHK-21- and NMuMG-derived virions were immunoblotted for gB-NT (mAb MG-2C10) plus ORF17 as a loading control (mAb 150-7D1), or for gB-C (mAb MG-4D11). The positions of uncleaved gB (gB-FL), its cleavage products (gB-N, gB-C) and ORF17 are marked.