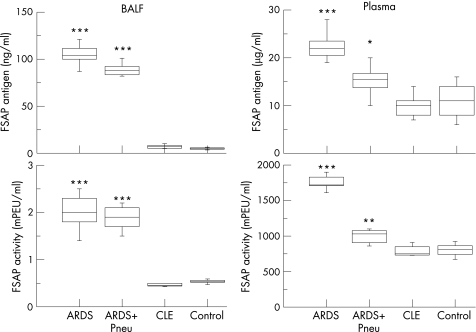
Figure 1 Quantitation of factor VII activating protease (FSAP) antigen and activity in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and plasma of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) compared with healthy controls and patients with cardiogenic pulmonary oedema. FSAP antigen level as assessed by ELISA (top panels) and FSAP activity as assessed by its single chain urokinase activating potency (bottom panels) in BAL fluid (left) and plasma (right) of healthy controls (n = 15) and of patients with extrapulmonary ARDS without pulmonary infection (ARDS; n = 15), ARDS with primary lung infection (ARDS + Pneu; n = 8) and with cardiogenic pulmonary oedema (CLE; n = 5) were quantitated. The box‐and‐whisker plots indicate the median, 1st and 3rd quartiles; the whiskers are extended to the most extreme value inside the 1.5‐fold interquartile range. *p = 0.016, **p = 0.009, ***p<0.001 ARDS vs healthy controls.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.