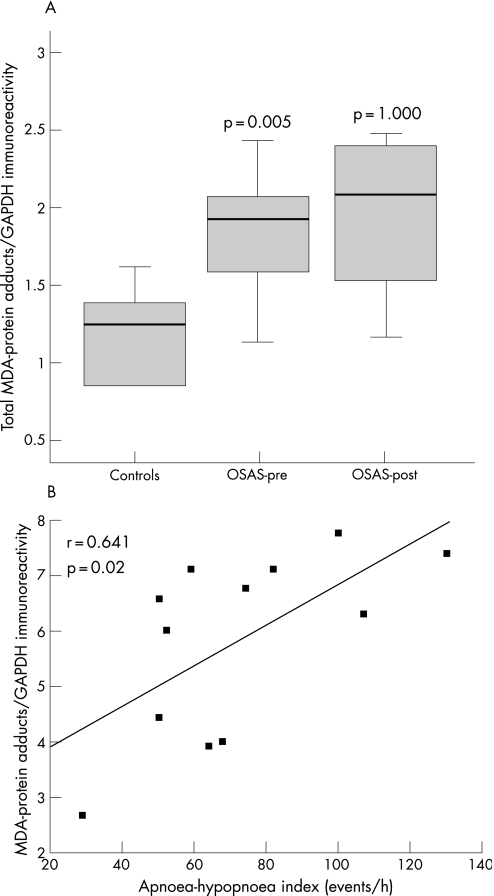
Figure 2 (A) Optical densities in the box plots are expressed as the ratio of the optical densities of total malondialdehyde (MDA)‐protein adducts to those of glyceraldehyde‐3‐phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). Standard box plots with median (25th and 75th percentiles) and whiskers (at minimum and maximum values) are shown. At baseline, total levels of MDA‐protein adducts were significantly greater in the external intercostal muscles of patients with severe obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome (OSAS) than in control muscles (median values 1.91 and 1.24, respectively, p = 0.005). Total muscle MDA‐protein adducts were not significantly modified after a 6‐month period of treatment with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) (median value 2.07, p = 1.0). OSAS‐pre, patients with OSAS before treatment with CPAP; OSAS‐post, patients with OSAS after 6 months of treatment with CPAP. (B) Overall, in patients with OSAS the ratio of the optical densities of total MDA‐protein adducts to those of GAPDH directly and significantly correlated with the apnoea‐hypopnoea index (events/h).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.