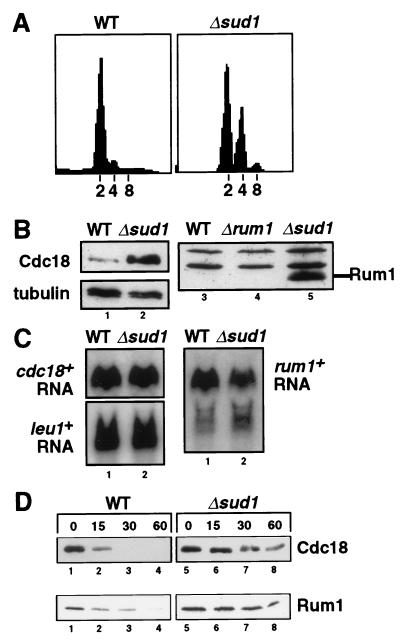
Figure 2.
sud1+ stops unwanted diploidization and is required for rapid degradation of both Cdc18 and the fission yeast CDK inhibitor Rum1. (A) DNA content of wild-type and Δsud1 cells was analyzed by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. The positions of normal haploid (2C), diploid (4C), and tetraploid (8C) DNA contents are indicated. (B) The abundance of Cdc18 and Rum1 proteins in wild-type, Δsud1, and Δrum1 strains was measured by immunoblotting with specific antibodies. (C) Northern blot analysis of cdc18+ and rum1+ mRNA transcripts in wild-type (lane 1) and Δsud1 cells (lane 2). The leu1+ mRNA was used as a loading control. PhosphorImager quantitation demonstrated that cdc18+ and rum1+ mRNAs were equally abundant in both strains. (D) Increased half-life of Rum1 and Cdc18 proteins in Δsud1 strains. HA-tagged forms of Cdc18 (Upper) and Rum1 (Lower) were expressed under the control of the weak nmt1 promoter in either wild-type cells (lanes 1–4) or Δsud1 cells (lanes 5–8). Degradation of Cdc18 and Rum1 was monitored after acutely repressing de novo synthesis with thiamine and cycloheximide.