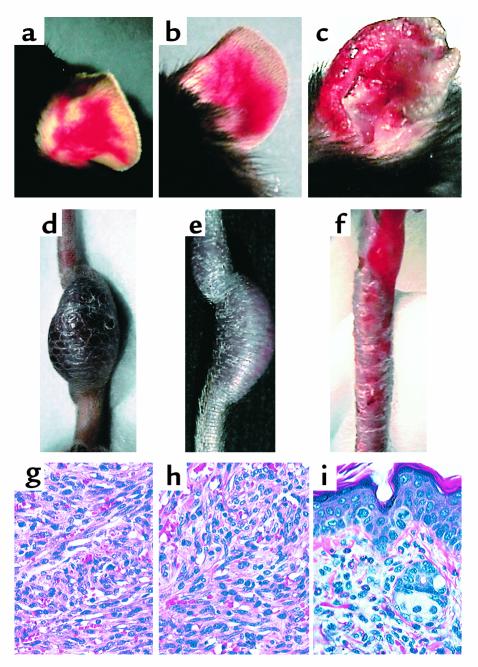
Figure 3.
Angiogenic and inflammatory lesions in CDVG, R2H and Δ22 transgenic mice. (a) Angiogenic lesions in the ear of a CDVG (line 19) mouse. (b) Angiogenic lesions in the ear of a R2H (line 24) mouse. (c) Erythematous, swollen, ulcerated ear lesions in a Δ22 (line 1) mouse. (d) Tail tumor in a CDVG (line 19) mouse. (e) Tail tumor in a R2H line 24 mouse. (f) Ulcerations and scales in the tail of a Δ22 (line 1) animal. (g) H&E-stained section of the tumor from the CDVG mouse shown in d. The tumor is moderately pleomorphic, and many spindle-shaped cells arranged in interlacing fascicles are present. Several slitlike vascular spaces often containing erythrocytes are observed. (h) H&E-stained section of the tumor from the R2H mouse shown in e. The cellular composition and the arrangement of spindle cells in fascicles is indistinguishable from that found in CDVG mice (e). (i) H&E-stained section of the ear of the Δ22 animal shown in c. The cellular infiltrate in inflamed ears consists mostly of granulocytes (eosinophils and neutrophils) and mononuclear cells.