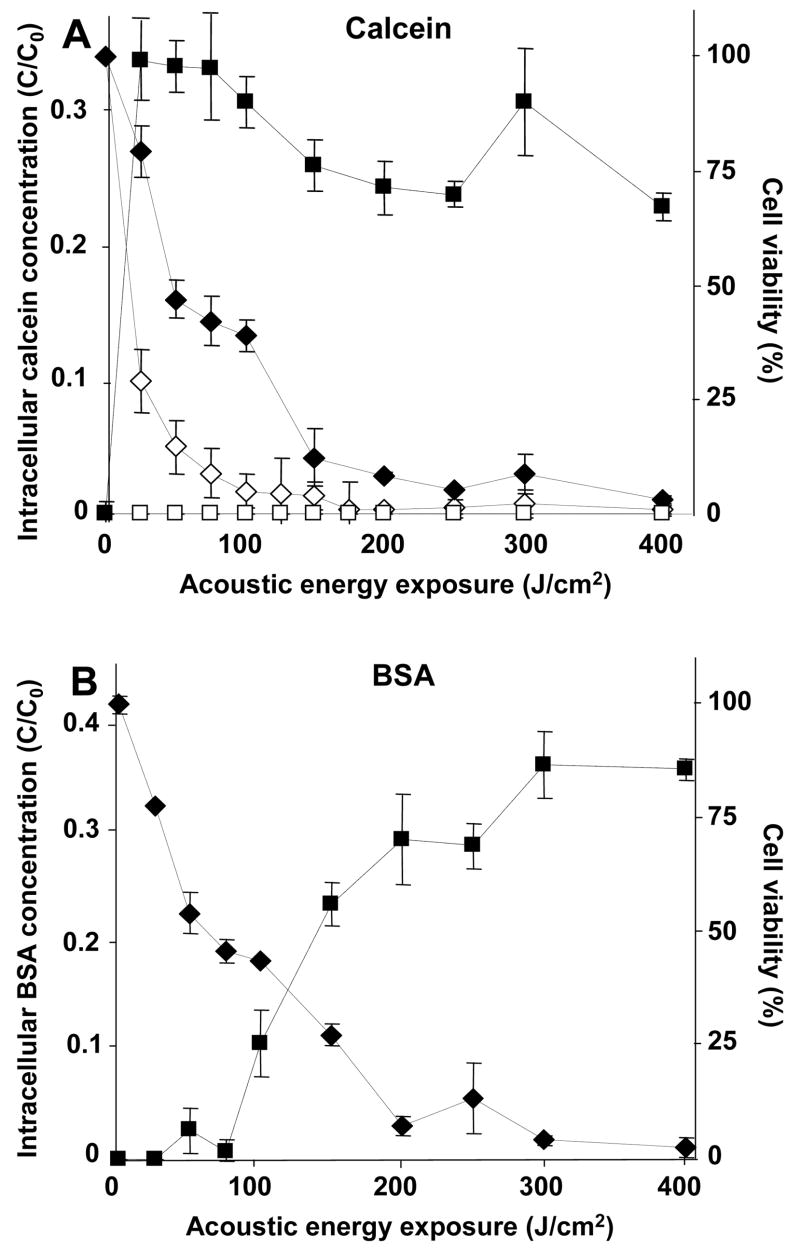
Figure 4.
Influence of the cell wall on intracellular uptake and cell viability as a function of energy exposure during sonication. The normalized intracellular concentration of a small molecule, calcein (A), and a macromolecule, BSA (B), is shown versus acoustic energy exposure. For the same population of cells, the cell viability is also shown. The black and white symbols represent data from the wild-type and wall-deficient algal cells, respectively. The square and diamond symbols represent intracellular concentration and cell viability, respectively. These data show that wild-type cells exposed to sonication take up large amounts of BSA, which contrasts with the lesser effects of electroporation, and that wall-deficient cells are easily killed by sonication and do not take up molecules at all. In (B), data are not shown for BSA uptake in wall-deficient cells, because (A) demonstrated that wall-deficient cells do not take up calcein and therefore are not expected to take up BSA either.