Figure 1.
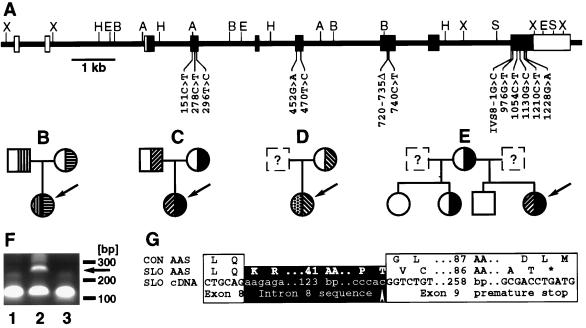
Mutations in the DHCR7 gene of patients with the SLOS. (A) Structure of the gene. Noncoding (open boxes) and coding exons (filled boxes) are shown. Restriction enzyme cleavage sites (A, AccI; B, BamHI; H, HindIII; S, SpeI; X, XhoI) and mutations are indicated. (B-E) Families with SLOS. The index patient is indicated by the arrow. Heterozygotes and homozygotes for mutations in the DHCR7 gene are shown. (B) Patient SLO8; mutations R404C (▥) and A247V (▤). (C) Patient SLO1; mutations V326L (▨) and W151X (▪). (D) Patient SLO6; mutations P51S (▩) and IVS8–1G>C (▧). (E) patient SLO2; mutations V326L (▨) and W151X (▪). (F) Abnormal reverse transcription-PCR-product (arrow) from fibroblasts from patient SLO5 (lane 2) not seen in cDNA from a control person (lane 1) and patient SLO9 (lane 3). Oligonucleotides c898s (GACCACTTCGGGTGGTACCTGGGC) and c999as (GACAGCTGCACGGGGTGGTACACC) are expected to give a 101-bp product. (G) Consequences of the splice site mutation found in patient SLO5. The amino acid sequence of a spliced transcript from a control person (CON AAS) is aligned with the amino acid sequence (SLO AAS) encoded by the transcript (SLO cDNA) from patient SLO5’s fibroblasts. The mutation (arrow) and the premature stop codon (∗) are indicated.