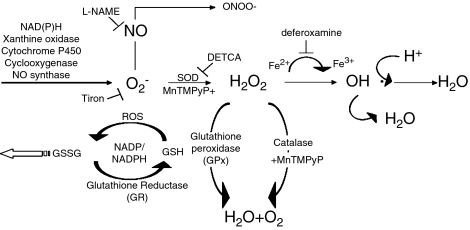
Figure 1.
Formation of oxygen-derived free radicals. Superoxide anions (O2−) can be generated from molecular oxygen, or by the action of xanthine oxidase, or of various enzymes. O2− can be scavenged by NO. It can also be converted to highly reactive oxygen species as peroxynitrite (ONOO−) when combined with NO, or H2O2 by SOD. H2O2 can be transformed to hydroxyl radicals by ferrous ions or converted to H2O by catalase and glutathione. Tiron scavenges O2− inside cells. DETCA inhibits SOD. Deferoxamine is an iron chelator that scavenges hydroxyl radicals. L-NAME inhibits NO synthase. MnTMPyP mimics the combined effect of SOD and catalase. DETCA, diethyldithiocarbamic acid; GSH, glutathione; GSSG, glutathione disulphide; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; L-NAME, Nω-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester hydrochloride; MnTMPyP, Mn(III)tetrakis(1-methyl-4-pyridyl)porphyrin pentachloride; NO, nitric acid; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SOD, superoxide dismutase; tiron, 4,5-dihydroxy-1,3-benzenedisulphonic acid.