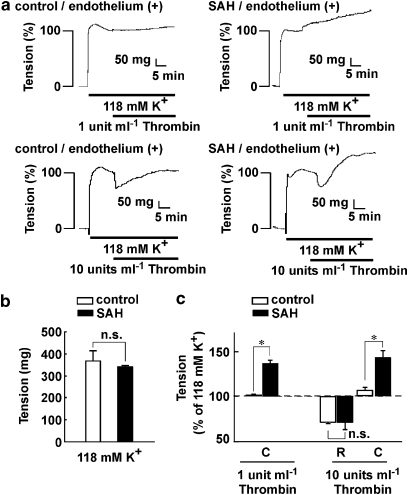
Figure 1.
Effect of thrombin on tension during contractions induced by 118 mM K+ in rings of the basilar artery with an intact endothelium. (a) Representative recordings showing the effects of 1 and 10 U ml−1 thrombin on the 118 mM K+-induced contraction in the basilar artery with an intact endothelium obtained from control and subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) rabbits. (b) The level of tension induced by 118 mM K+ depolarization in the basilar artery with an intact endothelium in control and SAH. The data are the mean±s.e.m. (n=7). n.s., not significantly different. (c) Summary of the maximal relaxation (R) and contraction (C) induced by 1 and 10 U ml−1 thrombin during the 118 mM K+-induced contraction in the basilar artery with an intact endothelium in control and SAH. The level of tension just prior to the application of thrombin during the 118 mM K+-induced contraction was assigned a value of 100%, and it is indicated by a dashed line. The contractile response to thrombin was evaluated 20 min after the application of thrombin. The data are the mean±s.e.m. (n=4). n.s., not significantly different. *P<0.05.