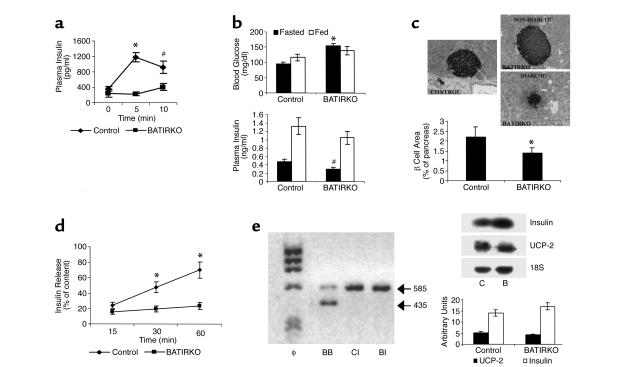
Figure 6.
BATIRKO male mice show an insulin-secretion defect. A representative insulin-secretion test is shown. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 7–12). *P < 0.001; #P < 0.005 (a). Blood glucose level (b)(upper panel) and blood insulin level (b) (lower panel) were determined in fasted and fed control and BATIRKO mice. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 25–30), *P < 0.000001, #P < 0.01 BATIRKO vs. control. Islet morphology was studied by immunohistochemical analysis in BATIRKO and control mice, as shown in Methods. Representative pancreatic sections from control and diabetic and nondiabetic 6-month-old BATIRKO mice stained for insulin are shown (c)(upper panels). β-cell area was measured by immunohistochemical analysis. Results are expressed as the percentage of the total surveyed area containing cells positive for insulin and are mean ± SEM (n = 10). *P < 0.01. Both diabetic and nondiabetic animals were studied (c)(lower panel). Insulin secretion in control and BATIRKO isolated islets is shown. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 4). *P < 0.05 (d). RT-PCR analysis of total RNA from BAT of BATIRKO mice (BB) and islets from control (CI) and BATIRKO mice (BI) was performed, and IR expression was studied (e)(left panel). Total islet RNA from control (C) and BATIRKO (B) mice was submitted to Northern blot analysis and hybridized with labeled insulin and UCP-2 cDNAs. A representative experiment out of three is shown. Densitometric analysis was performed using 18S ribosomal rRNA for normalization (e)(right panels).