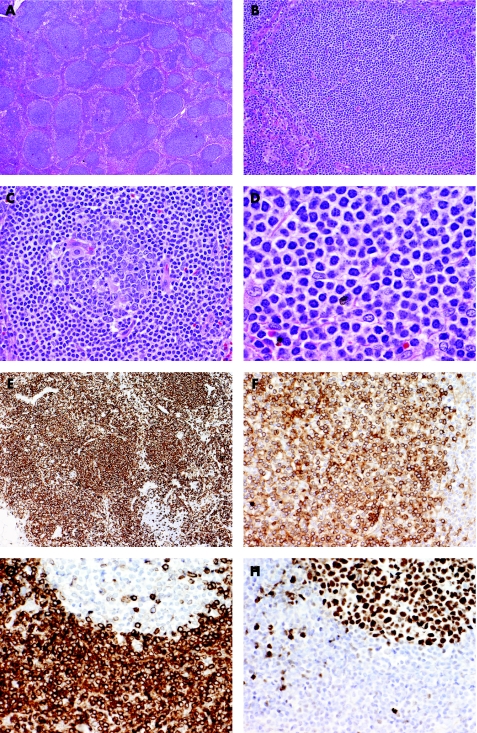
Figure 2 Nodal marginal zone lymphoma arising in a patient with chronic HCV hepatitis. (A) Although there is partial preservation of the lymph node architecture, there are numerous nodules/follicles primarily composed of small lymphoid cells. (B&C) Some of the follicles are entirely composed of small lymphoid cells mimicking primary follicles (B), but others contain a small reactive germinal centre and neoplastic cells occupy the mantle and marginal zones (C). (D) High power view shows that the neoplastic cells are mostly small lymphocytes with moderate amount of clear cytoplasm (so‐called monocytoid appearance). (E&F) Immunohistochemistry shows that vast majority of the neoplastic cells within the follicles but also in the interfollicular areas are CD20 B cells (E) which express immunoglobulin kappa light chain (F). (G&H) The neoplastic B cells have the typical phenotype of marginal zone B cells expressing BCL2 (G) but not BCl6 (H). Note that residual follicles express BCL6 but not BCL2.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.