Table 2.
An overview of RNA ligation schemes using RNA ligase 1 (RNL1) or RNA ligase 2 (RNL2)
| Ligation type | Ligation structure | Ligation conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Single-stranded RNAs ligation with RNL1 |  |
Molecule I: RNA Molecule II: RNA or DNA |
| Splint ligation with RNL1 | 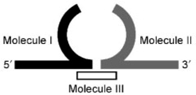 |
Molecule I: RNA or DNA Molecule II: RNA Molecule III: DNA Resulting hairpin length <8 nt |
| Y-ligation with RNL1 | 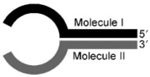 |
Molecule I: RNA Molecule II: RNA or DNA Resulting hairpin length <15 nt |
| Nick ligation with RNL2 |  |
Molecule I: RNA Molecule II: RNA or DNA Molecule III: RNA or DNA |
The directionality of the ligated nucleic acid strands are denoted by the non-ligated end of each strand. ‘Ligation type’ column includes a common name for a particular ligation reaction and RNA ligase type to be used for a particular ligation. RNA Ligase 1, and RNA Ligase 2 are abbreviated with RNL1 and RNL2, respectively. The ‘Ligation structure’ column provides a schematic representation of the RNA structure to be ligated. The ‘Ligation conditions’ column lists the combinations of nucleic acids resulting in an efficient ligation (107,109).
