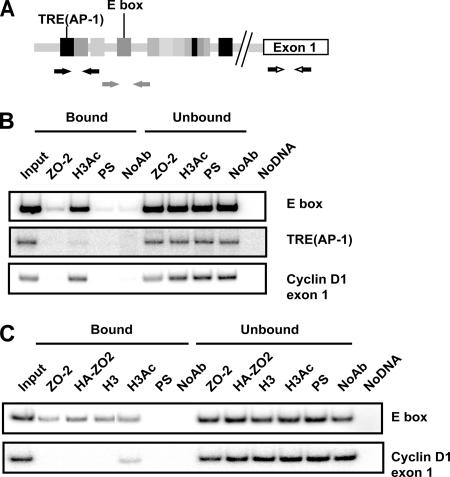
Figure 5.
ZO-2 associates in vivo to an E box element in the cyclin D1 promoter. (A) Schematic localization of specific primers used for PCR reactions in ChIP assays designed for the dog cyclin D1 promoter. Amplification of exon 1 was used as a negative control. (B) ChIP assays performed in sparse MDCK cells reveal the association of ZO-2 with an E box and not to the TRE(AP-1) element also present in the cyclin D1 promoter. The sizes of the amplified regions are 269 base pairs for the E box region, 200 base pairs for the TRE(AP-1) area, and 200 base pairs for exon 1. In this and the following ChIP assays, positive controls with H3Ac or H3 and negative controls with preimmune serum (PS) and no antibody (NoAb) were included. Input DNA, bound, unbound and no DNA fractions were amplified with the same set of primers as additional quality controls. (C) ChIP assay to detect recombinant ZO-2 were performed in cells that overexpress ZO-2 (pGW1-HA-ZO-2). Immunoprecipitates done with antibodies against ZO-2 and HA confirm the interaction of native and transfected ZO-2 (HA-tagged ZO-2) with the E box. Representative images of radioactive PCR products are shown. At least two independent experiments were performed for all ChIP assays.