Fig. 2.
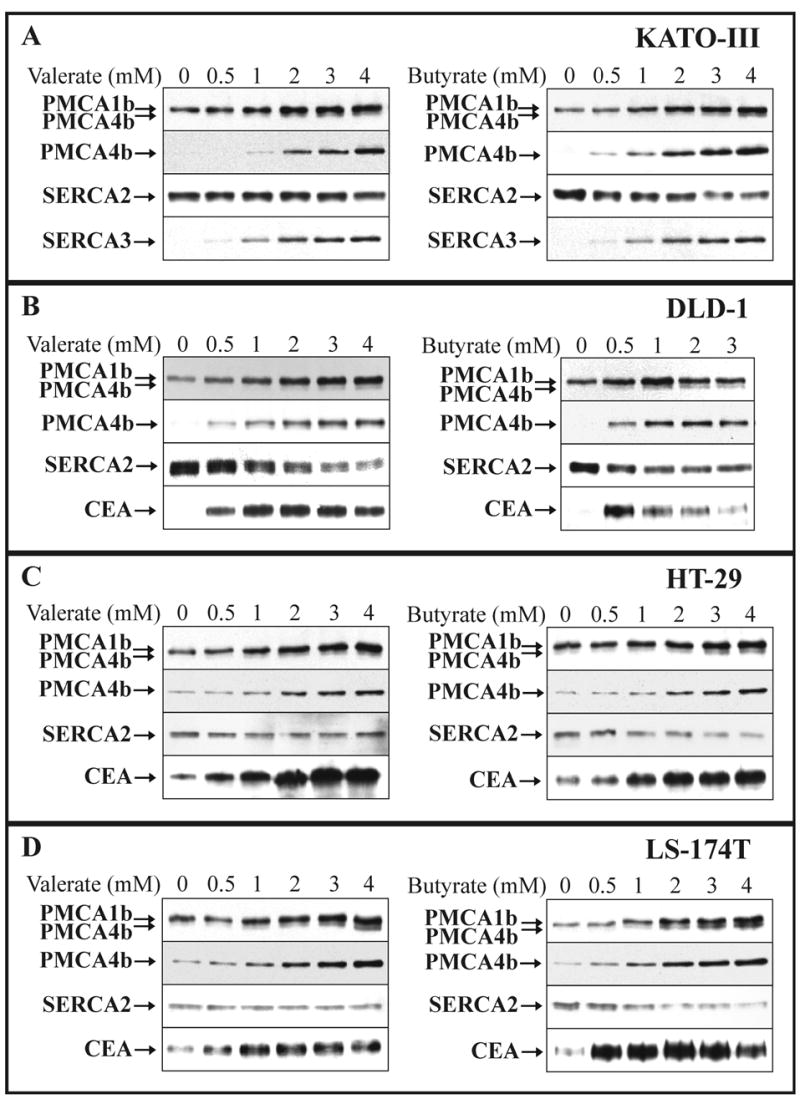
SCFA-induced modulation of PMCA expression in various gastric/colon cancer cell lines: concentration dependence.
KATO-III (A), DLD-1 (B), HT-29 (C) and LS-174T (D) cells were cultured in the presence of various concentrations of Na+-valerate or Na+-butyrate, as indicated on the panels. Total cellular protein lysates were prepared from all treatments at day 3 for KATO-III, DLD-1 and HT-29, and at day 2 for LS-174T cells. Equal amounts of cellular proteins (from 20 to 50 μg/lane, depending on the cell lines and the antibody used for immunostaining) were loaded onto the SDS-polyacrylamide gels, electroblotted and immunostained for overall PMCA (5F10) and PMCA4b (JA3) expressions. The expression of the ubiquitous SERCA2 pump, and that of various established differentiation markers (CEA and/or SERCA3) were monitored in parallel.
Treatment of the four cancer cell lines with these differentiation-inducing SCFAs led to the marked up-regulation of PMCA4b expression and to a less pronounced induction of PMCA1b expression.
