Fig. 5.
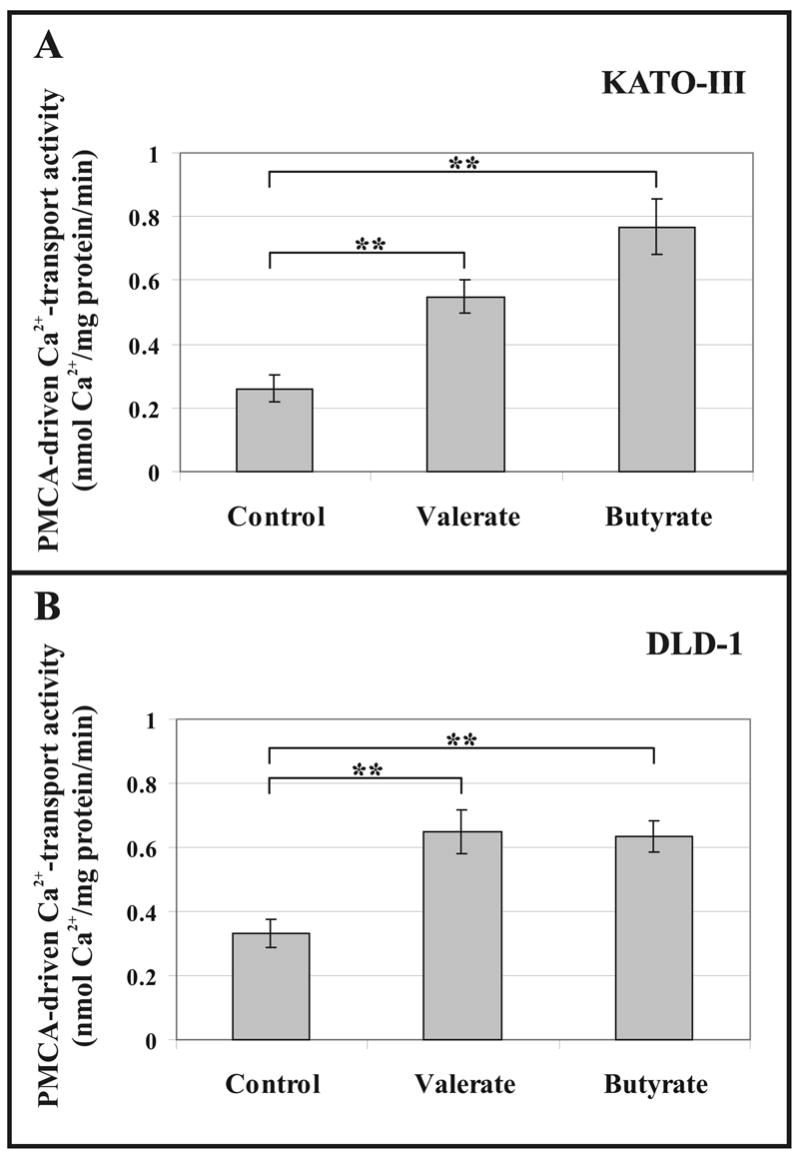
Up-modulated PMCA-driven Ca2+ transport activities of microsomal membranes from SCFA-treated KATO-III and DLD-1 cells.
KATO-III cells (A) were treated for 5 days with 3 mM Na+-valerate or 3 mM Na+-butyrate. DLD-1 cells (B) were treated for 5 days with 3 mM Na+-valerate or 2 mM Na+-butyrate. Untreated cells were used as controls. Maximal PMCA-driven Ca2+ transport activities were determined for each microsomal membrane preparation at saturating Ca2+ (8.1 μM free Ca2+) and calmodulin (1174 nM) concentrations.
The bars in panels (A) and (B) represent the means ± S.D. of 6-9 determinations from three independent experiments. Statistical significance is denoted by **p<0.01.
SCFA-induced differentiation resulted in up-regulated PMCA-driven Ca2+ transport in both cell lines.
