Figure 2 (a, b).
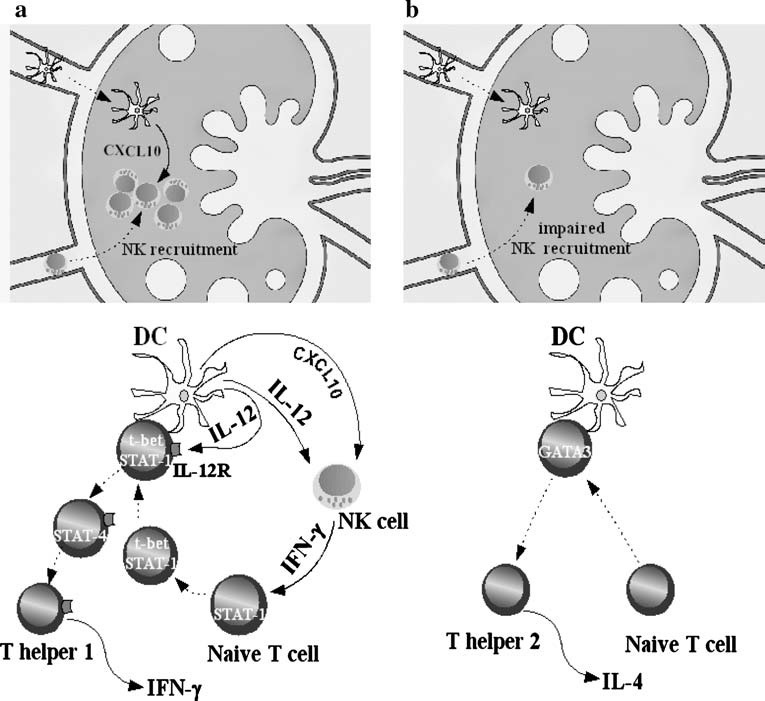
Dendritic cells shape T lymphocyte responses. (a) DCs migrating to the lymph node participate in NK recruitment by producing the CXCR3 ligand CXCL10. NK trafficking into inflamed lymph nodes is necessary for efficient priming of type 1 T lymphocytes. During antigen presentation, IFN-γ released by NK allows naïve T lymphocytes to be activated by IL-12 through the induction of IL-12 receptor. Under these conditions, DCs deliver signal 1 (MHC-peptide complex engaging TCR), signal 2 (DC costimulatory molecules CD80 or CD86 engaging CD28 on T lymphocyte surface) and signal 3 (STAT-4 activation by IL-12). (b) In ATP-conditioned DCs, simultaneous inhibition of IL-12 and CXCL10, but not IL-10 production, impairs the development of type 1 responses: reduced NK recruitment and antigen presentation in the absence of IL-12, but in the presence of IL-10, favours T helper 2 and/or T regulatory 1 differentiation.
