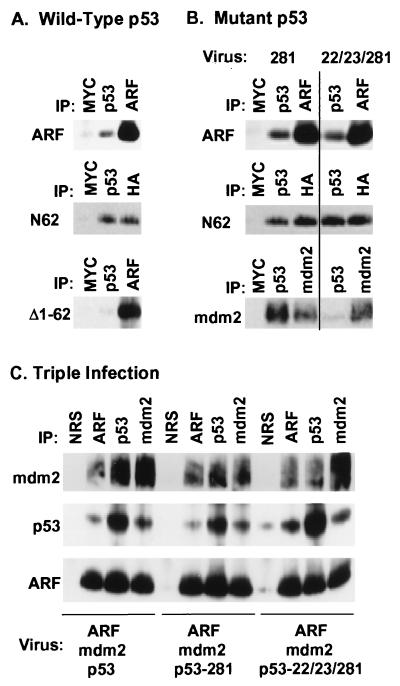
Figure 2.
Functional p19ARF binds to both mdm2 and p53 and can form ternary complexes. (A) Sf9 cells coinfected for 48 hr with baculoviruses encoding wild-type p53 and either p19ARF or the indicated p19ARF mutants were lysed and precipitated with control antibody to myc (9E10), p53 (PAb 421), affinity-purified antibody to the ARF C terminus, or anti-HA (to detect HA-tagged N62). Proteins in immune complexes separated on denaturing gels were transferred to filters and detected by immunoblotting with anti-ARF or anti-HA (for N62). (B) Similar experiments to those shown in A were performed using the indicated p53 mutants (top two panels). Sf9 cells were also coinfected with the indicated p53 mutants and mdm2 (Bottom) to document the inability of the 22/23/281 mutant to bind mdm2. Proteins precipitated with PAb421 or antibody 2A10 to mdm2 were electrophoretically resolved, transferred and blotted with 2A10. (C) Sf9 cells infected with the viruses indicated below each panel were lysed and incubated with nonimmune serum (NRS), antibodies to the ARF C terminus, PAb421 (p53), or antibody 2A10 (mdm2) as indicated at the top of each lane. Resolved proteins were blotted with antibodies to mdm2 (Top), p53 (Middle) or ARF (Bottom) as above.