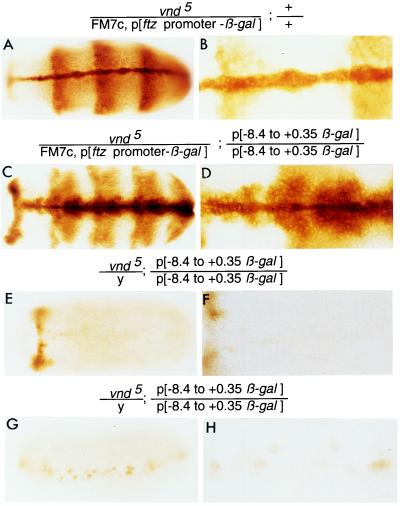
Figure 6.
vnd/NK-2 protein, directly or indirectly, activates the expression of the vnd/NK-2 gene. Expression of the β-gal reporter gene depends on functional vnd/NK-2 protein. (A and B) A female embryo with the genotype vnd/NK-2/FM7c, p[ftz promoter-β-gal]; +/+. The pattern of expression of β-gal is due to the p[ftz promoter-β-gal] insert in the FM7c balancer chromosome. (C and D) A female embryo with genotype vnd5/NK-2/FM7c, p[ftz promoter-β-gal]; p[−8.4 to +0.35 vnd/NK-2-β-gal]/p[−8.4 to +0.35 vnd/NK-2-β-gal]. The FM7c balancer chromosome contains a wild-type vnd/NK-2 gene and a DNA insert containing regulatory DNA from the ftz gene ligated to a β-gal reporter gene. The pattern of expression of β-gal protein is a composite of the vnd/NK-2 and ftz patterns of expression and etopic expression of β-gal along the ventral midline due to a positional effect on β-gal expression from the ftz regulatory DNA–β-gal reporter gene. (E–H) Male embryos with the vnd5 mutant gene and the homozygous P-element construct p[−8.4 to +0.35 β-gal] inserted in the second chromosome express little β-gal protein because mutant embryos lack wild-type functional vnd/NK-2 protein. All embryos are stage 11 embryos except the embryo in G, which is stage 12. The magnification of each embryo is higher in the right panel than in the left panel.