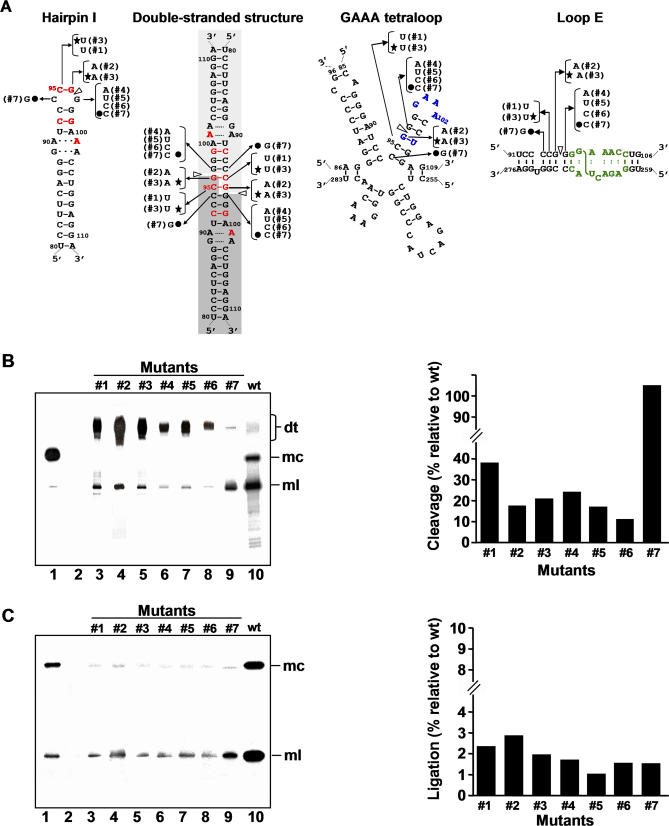
Figure 5. Processing in A. thaliana of Dimeric CEVd Transcripts with Mutations in the Central Positions of the Upper CCR Strand.
(A) Alternative foldings that can form the upper or both CCR strands: hairpin I/double-stranded structure in which red fonts denote nucleotides conserved in the family Pospiviroidae and light and dark gray backgrounds the two symmetric halves of the double-stranded structure (left), multibranched conformation with a GAAA-capped hairpin in which blue fonts denote conserved nucleotides in the genus Pospiviroid (center), and extended conformation containing a bulged-U helix adjacent to the loop E motif in which green fonts denote characteristic nucleotides by comparison with that of PSTVd [27] and the S-shaped line the UV-induced cross-link (right). White arrowheads mark the cleavage sites, and continuous and broken lines between nucleotides represent Watson-Crick and non-canonical base pairs, respectively. Nucleotide substitutions specific to each mutant (#1 to #7) are indicated on the alternative foldings, with filled circles and stars identifying the two double substitutions.
(B) Left panel. Northern blot analysis of viroid-enriched RNAs separated by single denaturing PAGE, transferred to a membrane and hybridized with a radioactive riboprobe for detecting CEVd (+) strands. Lane 1, CEVd-infected gynura; lane 2, non-transformed A. thaliana. Lanes 3 to 9, transgenic A. thaliana expressing dt CEVd (+) RNAs with different mutations (#1 to #7, respectively). Lane 10, transgenic A. thaliana expressing dt CEVd (+) RNA wild-type (wt). Positions of dt, mc, and ml CEVd RNAs are indicated. Right panel. Histograms that represent cleavage of each mutant relative to the wt sequence.
(C) Left panel. Northern blot analysis of viroid-enriched RNAs, the same as in panel (B) left, separated by double PAGE. Right panel. Histograms that represent ligation of each mutant relative to the wt sequence. Histogram values were estimated as detailed in Materials and Methods. Cleavage and ligation values of the wt sequence were 95% and 23%, respectively.