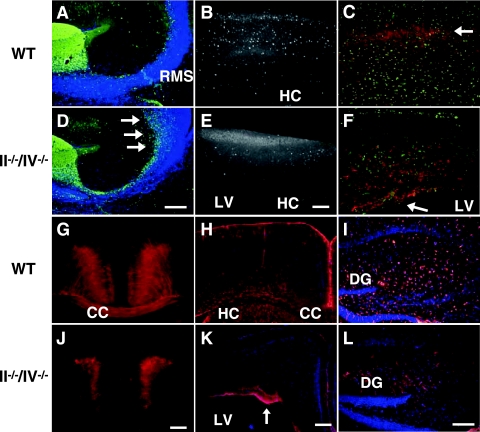
FIG. 2.
Polysialic acid is required for cerebral cortex development. (A and D) Calretinin expression in olfactory neuron precursors (green) of P10 mice. Arrows indicate accumulated cells near the SVZ. (B and E) CaBP (white) marks GABAergic interneurons in a 1-month-old cortex. (C, F, G, and J) Nonphosphorylated neurofilament (red) marks pyramidal cells in cortical layers II and III and V and VI in sagittal sections (C and F) and coronal sections (G and J) of 1-month-old mice. In II−/−/IV−/− mice, neurofilament-expressing cells remained near the ventricular zone (arrow in panel F). Nissl substance staining (green) shows the distribution of neurons (C and F). (H, I, K, and L) Distribution of glial cells expressing GFAP (red) in coronal sections of the cortex (H and K) and hippocampal sagittal sections (I and L) of 1-month-old mice. Note that the number of astrocyte-like cells was decreased in the hippocampus of II−/−/IV−/− mice (L). Panels A to C and G to I show WT mice, and panels D to F and J to L show II−/−/IV−/− mice. CC, corpus callosum; DG, dentate gyrus; HC, hippocampus; LV, lateral ventricle. Bars, 0.2 mm.