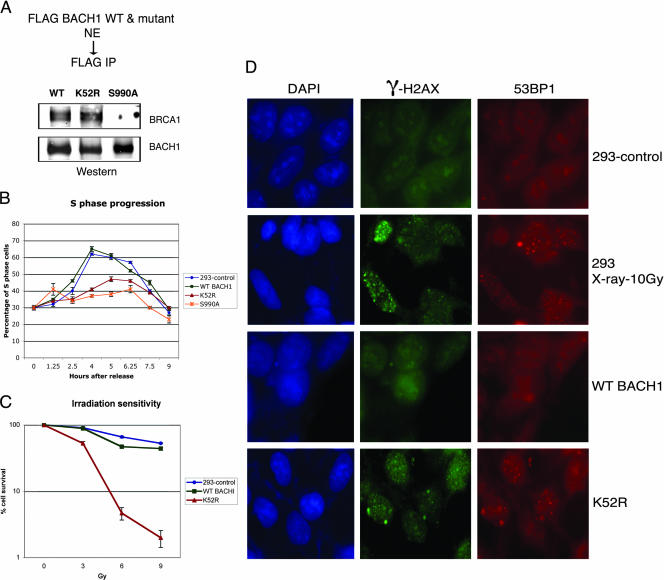
FIG. 6.
Cells expressing mutations in BACH1 helicase display a delay in S-phase progression and increased sensitivity to ionizing radiation. (A) Nuclear extracts from FLAG-WT BACH1, FLAG-K52R (helicase mutant), and FLAG-S990A were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody, and the fractions were analyzed by Western blotting with the antibodies shown to the right of the panel. (B) Control 293, FLAG-WT BACH1, FLAG-K52R, and FLAG-S990A cells were synchronized at G1/S with aphidicolin and released into S phase, and the cell cycle progression was monitored at the indicated time points after release by flow cytometric analysis of the total DNA content. The percentage distribution of cells in G1, S, and G2/M phases of the cell cycle as determined by PI staining is shown. (C) Mutation in BACH1 (K52R) result in enhanced sensitivity to ionizing radiation compared to control 293 or WT BACH1 cells. (D) 53BP1 and γ-H2AX foci formation were studied in WT BACH1 and K52R cells. Nonirradiated 293 cells (negative control), irradiated (10 Gy) 293 cells (positive control), and WT BACH1 and K52R cells were stained by immunofluorescence with antibodies against 53BP1 and γ-H2AX as described in Materials and Methods. As a control, cells were stained with DAPI to mark the nuclear domain.