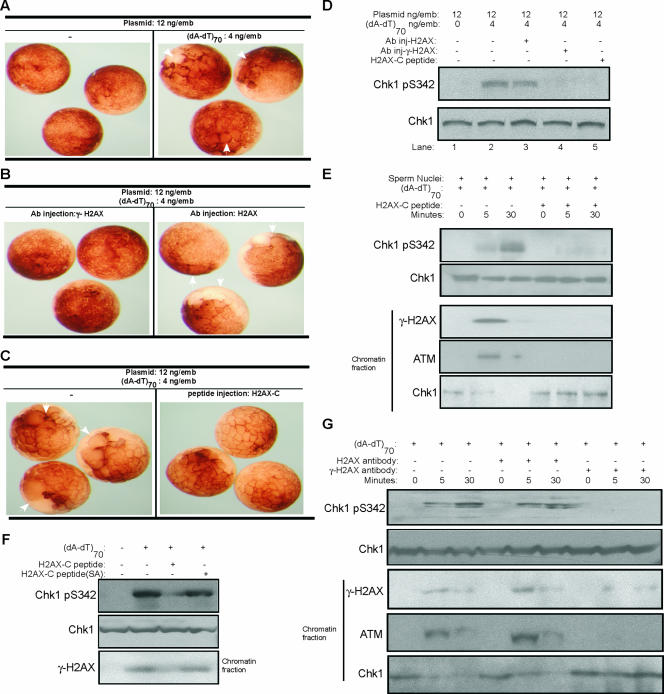
FIG. 5.
Phosphorylation of H2AX is required for threshold DNA to promote DNA damage-induced checkpoint activation. (A) One blastomere of each two-cell Xenopus embryo was microinjected with 12 ng of plasmid DNA/μl with or without (dA-dT)70 and then visualized by microscopy. White arrows indicate the injected blastomeres that display delayed cleavage divisions due to cell cycle arrest, compared to the control uninjected sites. (B) One blastomere of each two-cell Xenopus embryo was microinjected with 12 ng of plasmid DNA/μl, 4 ng of (dA-dT)70/μl, and antibody against γ-H2AX or H2AX. Embryos were then visualized by microscopy. White arrows indicate the injected blastomeres that displayed delayed cleavage divisions due to cell cycle arrest. (C) One blastomere of each two-cell Xenopus embryo was microinjected with 12 ng of plasmid DNA/μl and 4 ng of (dA-dT)70/μl, with or without peptide encoding the Xenopus COOH terminus of H2AX (CKKSSQQSQEY). Embryos were then visualized by microscopy. White arrows indicate the injected blastomeres that displayed delayed cleavage divisions due to cell cycle arrest. (D) Both blastomeres of two-cell Xenopus embryos were microinjected with plasmid DNA, (dA-dT)70, and antibody against human γ-H2AX, human H2AX, or a Xenopus H2AX COOH-terminal peptide, as indicated. Embryos were then lysed and subjected to immunoblotting for phospho-Chk1 and Chk1. (E) Xenopus egg extracts supplemented with buffer or a Xenopus H2AX COOH-terminal peptide were treated with (dA-dT)70 and sperm chromatin as indicated. Chk1 and phospho-Chk1 were measured by immunoblotting. Chromatin fractions were also isolated from the extracts and assayed by immunoblotting for γ-H2AX, ATM, and Chk1. (F) Xenopus egg extracts were treated with (dA-dT)70, a Xenopus H2AX COOH-terminal peptide, or a mutant peptide (CKKSSQQAQEY), in which the conserved Ser 139 phosphorylation site was changed to Ala. Chk1 and phospho-Chk1 were measured by immunoblotting. Chromatin fractions were also isolated from extracts and assayed by immunoblotting for γ-H2AX. (G) Xenopus egg extracts with (dA-dT)70 (4 ng/μl) and sperm chromatin (1,000/μl) were added with buffer, H2AX antibody, or γ-H2AX antibody. Samples were prepared at 0, 5, or 30 min after (dA-dT)70 addition, and Chk1 and phospho-Chk1 were measured by immunoblotting. Chromatin fractions were also isolated from extracts and assayed by immunoblotting for ATM, γ-H2AX, and Chk1.