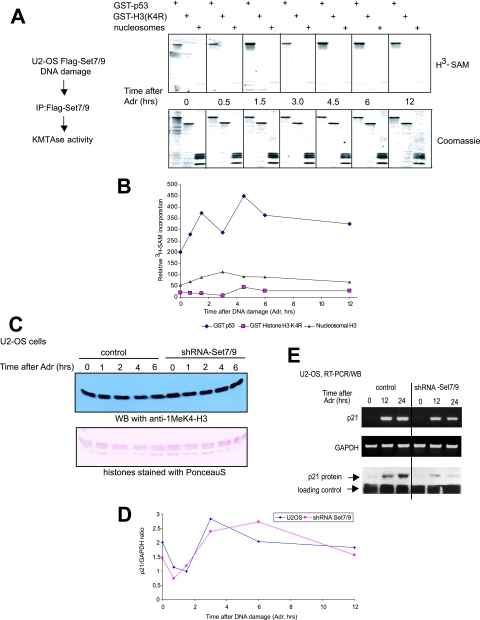
FIG. 4.
DNA damage does not activate nucleosomal HMTase activity of Set7/9. (A) Flag-Set7/9 immunopurified from U2-OS-Flag-Set7/9 cells, which were treated with DNA damage for the indicated periods of time, was tested in the methylation reaction in the presence of [3H]SAM with the following substrates: GST-p53300-393, GST-H31-27 (K4R), and nucleosomes purified from MCF-7 cells (top). The efficiency of protein methylation was determined by exposure of the 3H-labeled autoradiograph to film followed by densitometry. The protein levels were verified by Coomassie staining (bottom). (B) Quantification analysis of the experiment shown in panel A. (C) The levels of K4-H3 monomethylation in U2-OS versus U2-OS shRNA-Set7/9 cells. Cells were treated with 0.1 μM Adr for the indicated time periods, followed by chromatin extraction. Chromatin samples were probed for K4-H3 monomethylation by immunoblotting with specific antibody (Abcam). The input protein levels were analyzed by Ponceau-S staining. (D) The level of K4-H3 monomethylation in the p21 promoter is independent of the presence of Set7/9. A ChIP assay using K4H3-Me1-specifc antibody was performed on U2-OS and U2-OS shRNA-Set7/9 cells treated with 0.1 μM Adr. The levels of K4H3-Me1 in the promoter regions of p21 were determined by quantitative PCR using specific primers. The values represent the ratio of p21 to GAPDH signals. (E) p21 mRNA expression depends on Set7/9 activity. U2-OS cells stably infected with either scrambled shRNA (control) or vectors expressing shRNA-Set7/9 (shRNA-Set9) were treated with 0.5 μM Adr for 0, 12, and 24 h to induce DNA damage. Total RNA from these cells was then isolated, converted into cDNA by reverse transcriptase and analyzed for the presence of the p21 coding sequence by PCR using specific primers. GAPDH signal served as a loading control. In parallel, the same samples were subjected to Western blot analysis to measure the levels of p21 protein.