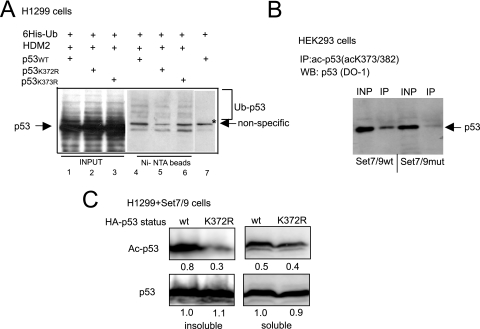
FIG. 5.
p53 acetylation is impaired in the absence of K372 methylation. (A) The methylation-deficient mutant of p53 does not exhibit increased ubiquitination in the absence of DNA damage. H1299 cells were transiently transfected with vectors expressing His6-ubiquitin and either p53 wild type or K372R methylation- or K373R acetylation-defective mutants. These cells were also transfected with HDM2-expressing plasmid where indicated. After incubation with proteosomal inhibitor MG132 for 12 h, cells were lysed with 8 M urea, and His6-ubiquitin-containing proteins were purified on Ni-NTA beads. The bead-bound proteins were eluted and analyzed by immunoblotting with p53-specific antibody (Ab-6). The positions of p53 and its ubiquitinated ladder are indicated. Lanes 1 to 3 (INPUT) represent 10% of the starting material, and lanes 4 to 6 (Ni-NTA beads) represent the bead-bound material eluted from Ni-agarose beads. (B) p53 acetylation depends on the KMTase activity of Set7/9. HEK293 cells stably expressing Set7/9 wild type or its catalytically impaired mutant (H297A) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with acetyl-p53-specific antibody. The resulting proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with (Ab-6) p53-specific antibody. Input (INP) lanes represent 10% of the starting material. (C) Mutation in p53 methylation site diminishes acetylation. H1299 (p53-) cells were transfected with vectors expressing either wild type or K372R nonmethylatable mutant p53. After DNA damage, cells were fractionated into soluble and insoluble chromatin fractions. The amounts of both p53 variants were normalized after Western blotting. The levels of acetylation in the wild-type and mutant p53 protein present in soluble and insoluble fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting with specific antibodies and quantified. The relative strength of p53 acetylation signal was quantified by arbitrarily setting the p53 wild-type signal as 1.