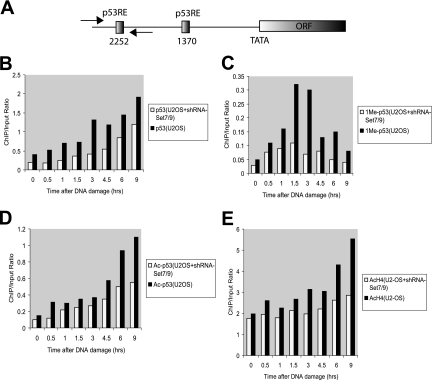
FIG. 7.
The loss of p53 methylation attenuates promoter acetylation of the p21 gene. (A) Schematic representation of the p21 gene. The binding sites of p53 and the transcription start site are indicated. Positions of the PCR primers used in the Q-PCRs are indicated. (B) The p21 promoter occupancy by p53 is decreased in the absence of Set7/9. A ChIP assay using p53-specific antibody was performed on U2-OS and U2-OS shRNA-Set7/9 cells treated with Adr for the indicated time periods. Immunoprecipitated DNA was analyzed by quantitative PCR for the presence of p21 and GAPDH using specific primers. Values were normalized to the GAPDH signal. (B, C, D, and E) ChIP analysis of the p21 promoter as performed in panel B for the presence of methylated p53 using methylated p53-specific antibody (C), acetylated p53 using acetylated p53-specific antibody (D), and acetylated histone H4 using acetylated histone H4-specific antibody (E).