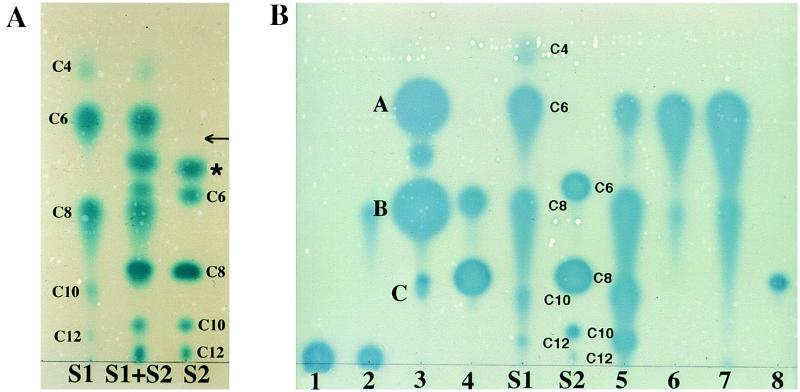
Figure 1.
TLC of acyl-HSLs. Samples were chromatographed on C18 reversed-phase thin-layer plates, developed with methanol/water (60:40, vol/vol), and the spots were visualized with the A. tumefaciens reporter strain. (A) Separation and detection of acyl-HSL standards. S1, 3-oxo-acyl-HSL standards; S2, 3-unsubstituted-acyl-HSL standards; S1 + S2, a mixture of the S1 and S2 standards. The acyl chain lengths are indicated for each compound. The asterisk marks an unknown active component. The arrow shows the position at which authentic N-butanoyl-l-HSL migrates. (B) Detection of acyl-HSLs produced by selected bacteria. Samples are from culture extracts of the following: 1, Rhizobium meliloti L5–30; 2, R. meliloti, YA2; 3, P. fluorescens 2-79; 4, Ralstonia solanacearum K60; 5, P. aeruginosa PAO1; 6, V. fischeri MJ1; 7, P. syringae, pv. tabaci 2024; and 8, Rhodobacter sphaeroides 2.4.1. Spots labeled A–C in lane 3 correspond to those compounds subjected to MS analysis as described in the text and in Fig. 3.