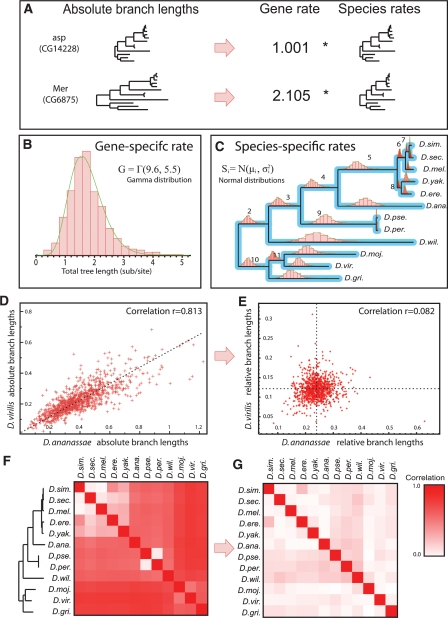
Figure 3.
Evolutionary rates decoupled into gene-specific and species-specific components. (A) Syntenic ortholog trees appear as scaled versions of a common species tree, and can be expressed as the product of a gene-specific rate and species-specific rates. (B) Gene-specific rates of 5154 fly orthologs follow a gamma distribution. (C) Species-specific rates for each lineage follow normal distributions. Means and standard deviations shown in Supplemental Figure S7. (D) Unnormalized (absolute) branch lengths are highly correlated. Lengths for D. virilis and D. ananassae since their last common ancestor across the 5154 orthologs show correlation r = 0.813. (E) Relative branch lengths become independent after normalization by the gene-specific rate (r = 0.082). (F) Correlations are high for all species pairs before normalization, except for very closely related species. (G) Relative lengths are uncorrelated for all species pairs, showing that gene-specific rate accounts for their initial dependencies.