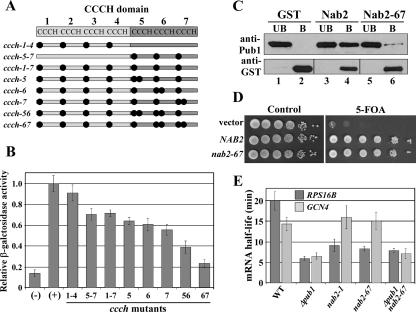
FIG. 5.
Amino acid substitutions within the Nab2 zinc finger domain abolish the interaction with Pub1 and decrease RPS16B mRNA stability. (A) Schematic of amino acid changes within the Nab2 CCCH domain. The specific amino acid residues changed in each Nab2 variant are detailed in Table S1 in the supplemental material. (B) Amino acid substitutions in the Nab2 CCCH domain decrease binding to Pub1. Two-hybrid SVL316 (EGY48; Invitrogen) cells expressing a transcription activation domain-Pub1 fusion (B42-Pub1; pSV545) were transformed with vector (pEG202) (-) or plasmids expressing wild-type (+) or the indicated variant CCCH Nab2 domains. Cells were grown in liquid medium containing galactose, and quantification of lacZ reporter activity, as a measure of the Pub1 interaction with the CCCH domain of Nab2, was determined by an in vitro β-galactosidase assay. The bar graph displays β-galactosidase activity relative to the wild-type CCCH domain, which was set to 1.0. Standard deviations in the data are indicated. (C) Nab2-67 shows a greatly decreased interaction with Pub1. GST (lanes 1 and 2), GST-Nab2 (lanes 3 and 4), or GST-Nab2-67 (lanes 5 and 6) was purified from E. coli and incubated with recombinant His6-Pub1. The unbound (UB) and bound (B) fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Pub1 and anti-GST antibodies. The bottom panel corresponds to the unbound and bound bands from different areas in the blot due to differences in protein sizes (26 kDa for GST alone and 95 kDa for GST-Nab2). (D) The nab2-67 mutant allele is functional. A plasmid shuffle technique was used to assess the ability of the nab2-67 mutant to replace the essential function of NAB2. NAB2 deletion cells (SVL544) maintained by a URA3 NAB2 plasmid (pSV877) were transformed with test plasmids carrying vector alone (pSV59), wild-type NAB2 (pSV572), or nab2-67 (pSV876). Samples were serially diluted and spotted onto a control plate (SC medium lacking Ura), where the wild-type NAB2 plasmid is retained, or selective medium (5-fluoroorotic acid [5-FOA]), where the wild-type NAB2 plasmid is lost and the only cellular copy of the essential NAB2 gene is provided by the test plasmid. Plates were incubated for 3 days at 30°C. Vector alone and wild-type NAB2 served as the negative and positive growth controls. (E) The stability of the RPS16B transcript is decreased in nab2-67 cells compared to wild-type (WT) cells. The half-lives of the RPS16B and GCN4 transcripts were determined using qRT-PCR as described in Materials and Methods.