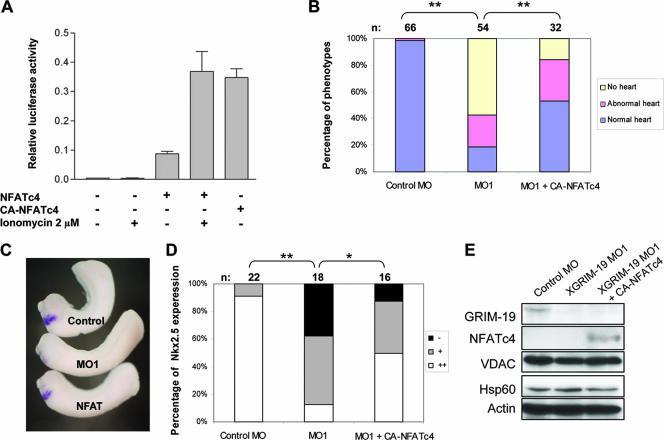
FIG. 6.
Rescue of heart deficiency by CA-NFATc4 in XGRIM-19 KD Xenopus embryos. (A) Comparison of NFATc4 and CA-NFATc4 activity in MCF-7 cells. MCF-7 cells were cotransfected with the pNFAT-TA-luc construct and either pcDNA3-NFATc4 or pcDNA3-CA-NFATc4. Cells were either left untreated or were treated with ionomycin to increase intracellular calcium levels. Dual luciferase assays were performed in triplicate, and the average luciferase activity from three independent experiments is shown, with error bars representing the standard deviations of the means. (B) CA-NFATc4 partially rescues the heart defect in XGRIM-19 KD embryos. Embryos were injected with control MO, XGRIM-19 MO1, or XGRIM-19 MO1 and CA-NFATc4 mRNA, as indicated. The percentages of embryos displaying heart phenotypes of normal, abnormal, and no heart are indicated as bars, and the number of embryos is shown on top (n) (**, P < 0.01). (C) Embryos were injected with control MO, XGRIM-19 MO1, or XGRIM-19 MO1 and CA-NFATc4 mRNA. Nkx2.5 mRNA was detected by in situ hybridization in these embryos at stage 28. (D) The percentages of embryos displaying an absence of (−), weak (+), or normal (++) Nkx2.5 expression are indicated as bars, and the number of embryos is shown on top (n) (**, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05). (E) Gene expression in embryos injected with control MO, XGRIM-19 MO1, or XGRIM-19 MO1 and CA-NFATc4 mRNA. Total embryo lysate at stage 28 was harvested and analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies against GRIM-19, NFATc4, VDAC, Hsp60, and actin, as indicated on the left.