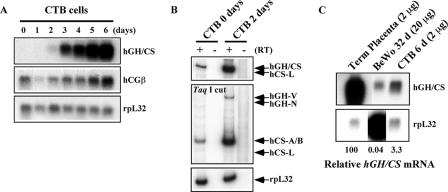
FIG. 3.
hGH-hCS genes were induced in ex vivo cultures of primary human placental CTBs. (A) Expression of the hGH cluster genes in primary placental CTB cell culture. The CTBs were cultured in the presence of second-trimester maternal serum for 6 days to induce spontaneous differentiation into syncytial cells capable of expressing the hGH-hCS genes. Total RNA was prepared from daily aliquots and analyzed by Northern blotting. Probes used are indicated to the right of the autoradiographs. (B) hCS-A, hCS-B, and hGH-V are expressed by the induced CTBs. RT-PCR analysis was conducted with RNA from CTBs at days 0 and 2 of culture. The PCR products were digested with TaqI and analyzed as described for Fig. 1C. The hCS-A and hCS-B mRNAs were detected at day 0, and their expression and that of hGH-V were induced by day 2. (C) Quantitative comparison of hGH-hCS expression levels among the placental model systems used in this study. Northern blot analysis was performed on total RNA from human term placenta, cultured primary CTBs at day 6 (CTB 6 d), and day 32 BeWo cells (BeWo 32 d). Relative hGH-hCS mRNA levels, estimated using the rpL32 signals as a loading control, are shown at the bottom.