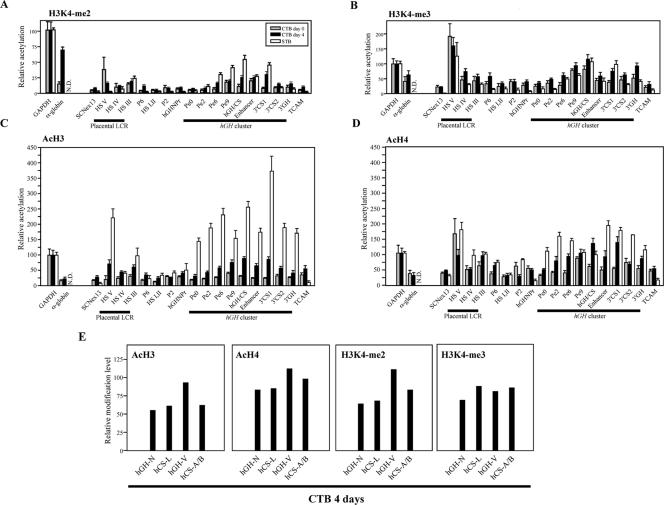
FIG. 6.
Histone modification at the hGH cluster and its LCR in primary CTBs before and after 4 days of differentiation. (A) Histone H3K4 dimethylation was established after day 4 of culture in primary CTBs. The amplimer positions are the same as those in Fig. 5A. Primary CTBs were isolated from human term placentas and cultured for 4 days in the presence of second-trimester maternal serum. The ChIP assay was performed with anti-dimethylated-histone H3K4 antibody as described for Fig. 5B on chromatin from freshly prepared CTBs (day 0) and after culture (day 4). For comparison, corresponding values for modifications of chromatin isolated from primary placental STBs, previously reported by us (32), are shown. (B) The histone H3K4 trimethylation pattern was largely preset in the freshly prepared, day 0 CTBs. The histone H3K4 trimethylation pattern was examined by ChIP with anti-trimethylated-H3K4 antibody, analyzed, and labeled. (C) Histone H3 acetylation was induced at the hGH locus during differentiation from CTBs to STBs. The histone H3 acetylation patterns were determined by ChIP with anti-acetylated-histone H3 antibody. (D) Histone H4 acetylation was induced at the hGH locus during differentiation of the CTBs. The histone H4 acetylation levels were investigated by ChIP with anti-acetylated-histone H4 antibody. (E) All genes in the hGH cluster were similarly modified in the day 4 CTBs. Histone modification levels at each cluster gene were examined by ChIP. The PCR analysis of the isolated DNA was performed with an amplimer set common to the five genes; the amplified products were digested with four restriction enzymes to distinguish each signal.